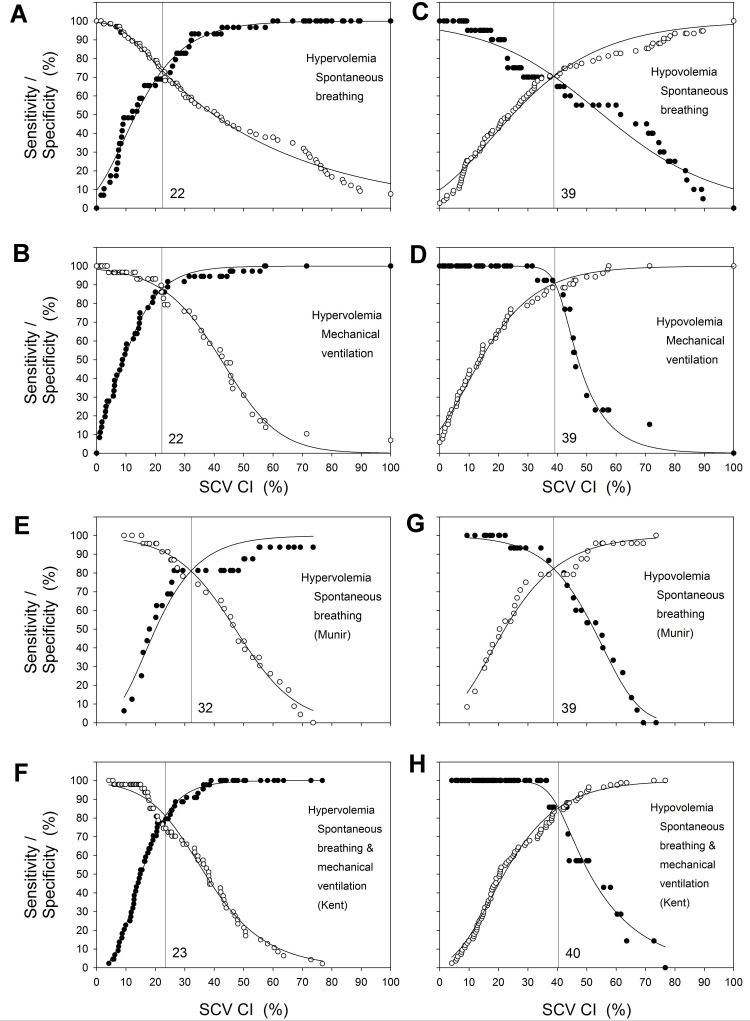
Figure 2.
Sensitivity and specificity plots for various SCV CI cut-offs as predictors for whether IVC CI is <20% or >50% for spontaneous breathing and ventilated encounters. Solid circles are sensitivity and open circles are specificity. The solid lines are the sigmoidal fit to the data constrained to maximum and minimum sensitivities and specificities of 100% and 0%, respectively. The SCV CI cut-off at which the sensitivity and specificity are equal is indicated by the vertical lines. Sensitivity and specificity plots for various SCV CI cut-offs as predictors for whether IVC CI is <20% for spontaneous breathing encounters (A), <20% for mechanically ventilated encounters (B), >50% for spontaneous breathing encounters (C), >50% for mechanically ventilated encounters (D). Sensitivity and specificity plots for various SCV CI cut-offs from data derived from published reports, as predictors for whether IVC CI is <20% for spontaneous breathing encounters for medical patients (Munir et al16) (E), <20% for spontaneous breathing and mechanically ventilated encounters for surgical ICU patients (Kent et al13) (F), >50% for spontaneous breathing encounters for medical patients (Munir et al16) (G), and >50% for a combination of spontaneous breathing and mechanically ventilated encounters for surgical ICU patients (Kent et al13) (H). For the data from Munir et al,16 collapsibility index ((max-min)/max) *100% was derived from (1-the ratio of min/max) for both SCV CI and IVC CI.