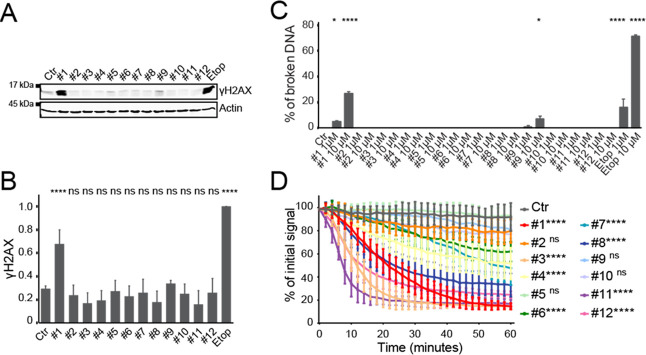
Figure 2.
Evaluation of DNA break capacity and histone evicting activity of hybrid structures 2–11 and parent compounds doxorubicin (1) and aclarubicin (12). (A) K562 cells were treated for 2 h with 10 μM of the indicated drugs, etoposide was used as a positive control for DNA double-strand breaks. γH2AX levels were examined by Western blot. Actin was used as a loading control, and molecular weight markers are as indicated. (B) Quantification of the γH2AX signal normalized to actin. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. Ordinary one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test; ns, not significant; ****P < 0.0001. (C) Quantification of broken DNA relative to intact DNA as analyzed by constant-field gel electrophoresis (CFGE). Etoposide was used as a positive control for DNA double-strand breaks. Results are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test; *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001 is indicated, all others are not significant. (D) Quantification of the release of fluorescent PAGFP-H2A from the photoactivated nuclear regions after administration of 10 μM of the indicated drugs. Results are shown as mean ± SD of 10–20 cells from at least three independent experiments. Ordinary two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test; ns, not significant; ****P < 0.0001. See also Figures S1 and S2.