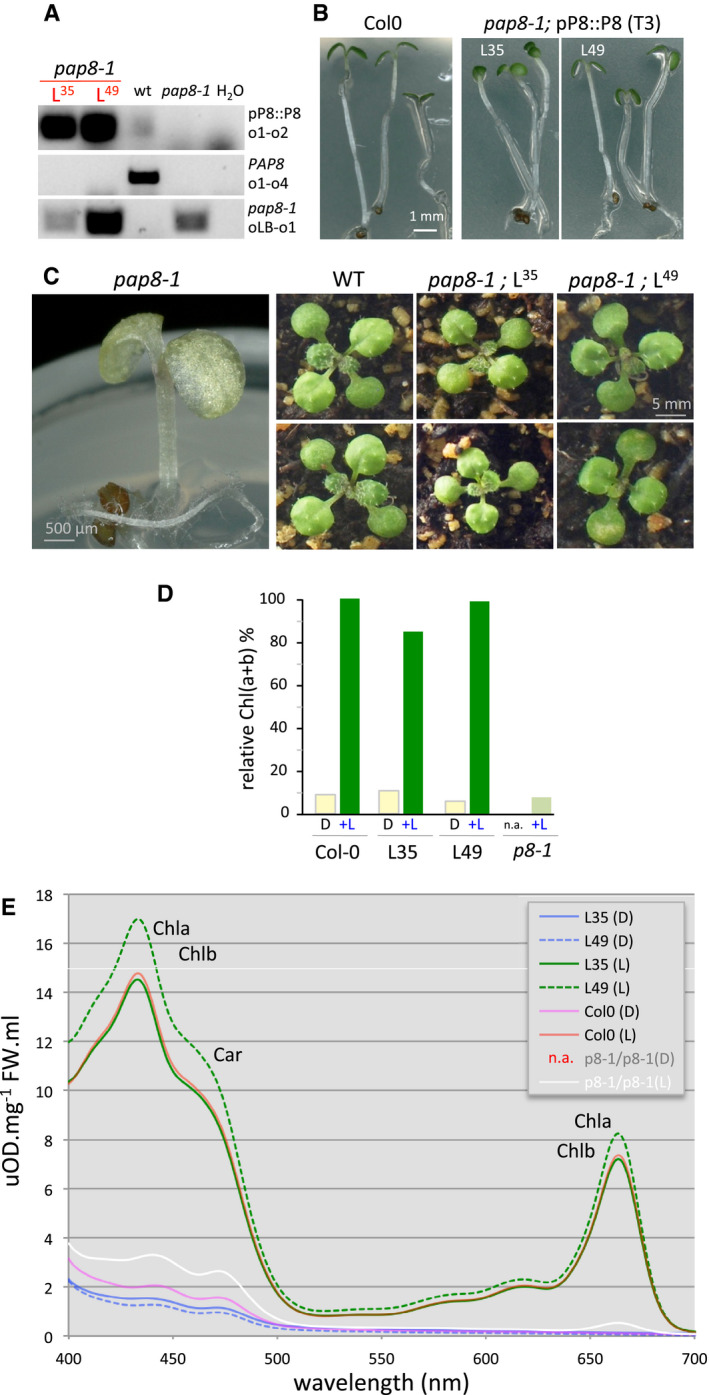
The construction used for complementation is pPAP8::PAP8
cds (pP8::P8 in short): PAP8 coding sequence under control of a 1.1‐kb upstream region used as promoter (see pBB389 in
Appendix Table S1 and Fig
2A for the description of the regulatory region used as promoter).
-
A
PCR on genomic DNA; L35, L49: Two independent “pBB389” transgenic lines; primers are the same as in Fig
1B and o4: op8i2_R.
-
B
Greening assay on wild type and rescued pap8‐1 homozygous plants from third generation transgenic lines (T3) grown in vitro 3 days in the dark followed with a 30‐h light treatment. L35 and L49 are two independent rescued lines.
-
C
Phenotypes of pap8‐1 homozygous plant grown in vitro, and two representative plants of wild type or pap8‐1/pP8::PAP8 (line L35 or line L49) grown on soil.
-
D
Content of total chlorophylls (Chl(a+b)) normalized to fresh weight and relative to wild type in the given genotypes grown in the dark (D) or grown in the dark followed with 30 h of white light treatment (+L); n.a. not applicable.
-
E
Spectrophotometric analysis of pigments: absorption spectra of acetone‐soluble extracts from seedling grown in vitro 3 days in the dark (D) or 3 days in the dark plus 30 h of white light (L) Col‐0, wild type; p8‐1/p8-1, homozygous mutant pap8‐1; L35 and L49, two lines of pap8‐1/pPAP8::PAP8; n.a., not applicable. Absorbance was normalized to fresh weight (FW); Chla, chlorophyll a; Chlb, chlorophyll b; Car, carotenoids.
Source data are available online for this figure.