Figure 2.
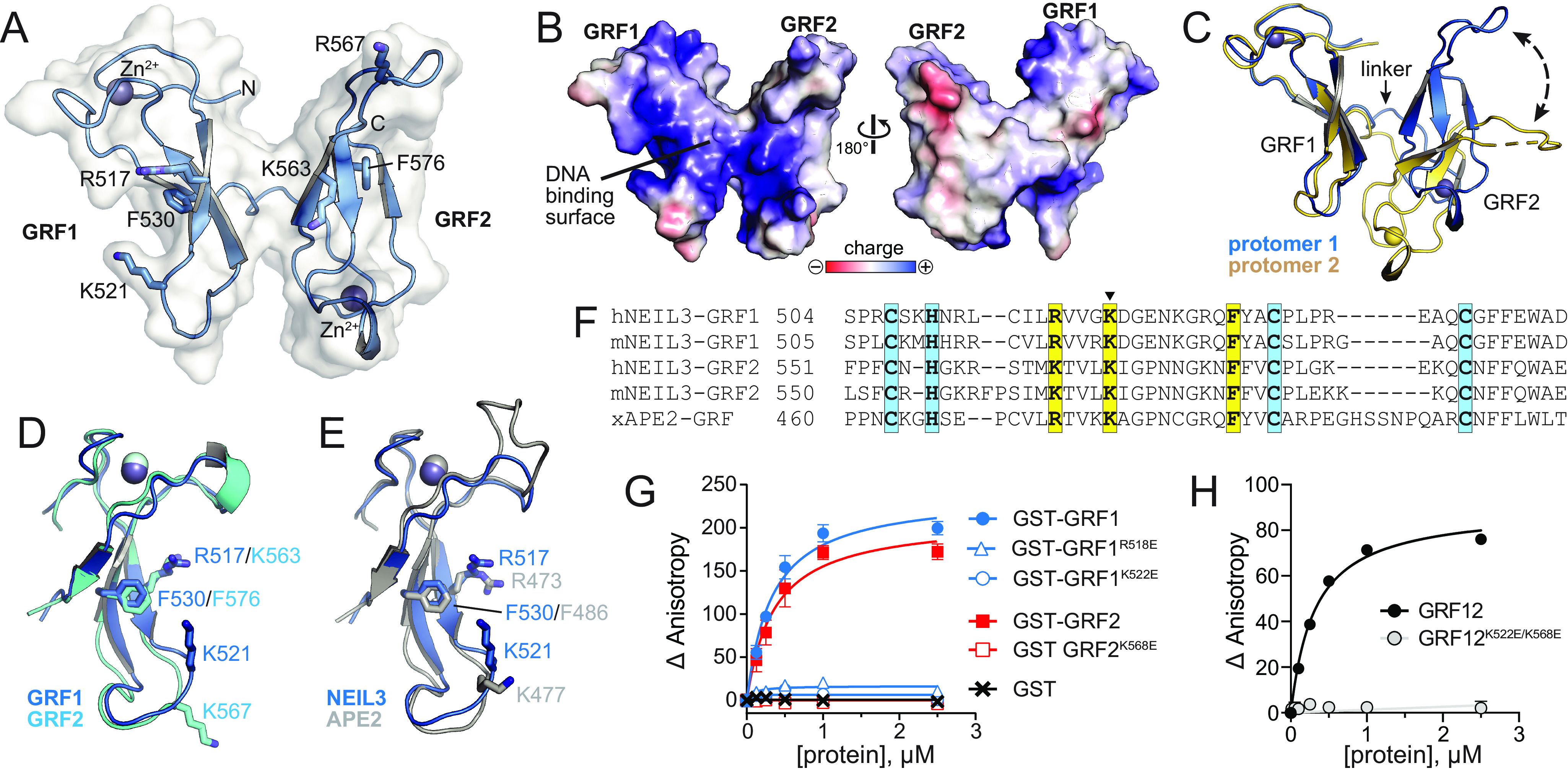
Crystal structure of hNEIL3 GRF domain. A, structure of one of the two protomers in the asymmetric unit. The molecular surface is shown in white, and the positions of several conserved DNA binding residues are indicated. B, The two faces of the GRF12 structure, colored by electrostatic potential. The image on the left is in the same orientation as in A. C, the two GRF12 molecules in the asymmetric unit, superimposed by GRF1. The difference in relative position of GRF2 is highlighted by a dashed arrow. D, superposition of GRF1 and GRF2. E, superposition of GRF motifs from hNEIL3 (blue) and xAPE2 (silver, PDB ID 5U6Z). F, structure-based sequence alignment of hNEIL3 and xAPE2 GRF structures, together with aligned sequences from mNEIL3. Zn2+-coordinating and DNA-binding residues are highlighted blue and yellow, respectively. The lysine mutated in the GRFmut constructs is marked with a triangle. G and H, DNA binding of individual mNEIL3 GRF motifs as GST fusion proteins (G) and the tandem, untagged GRF12 domain (H). The data are means ± S.D. (n = 3).
