Figure 1.
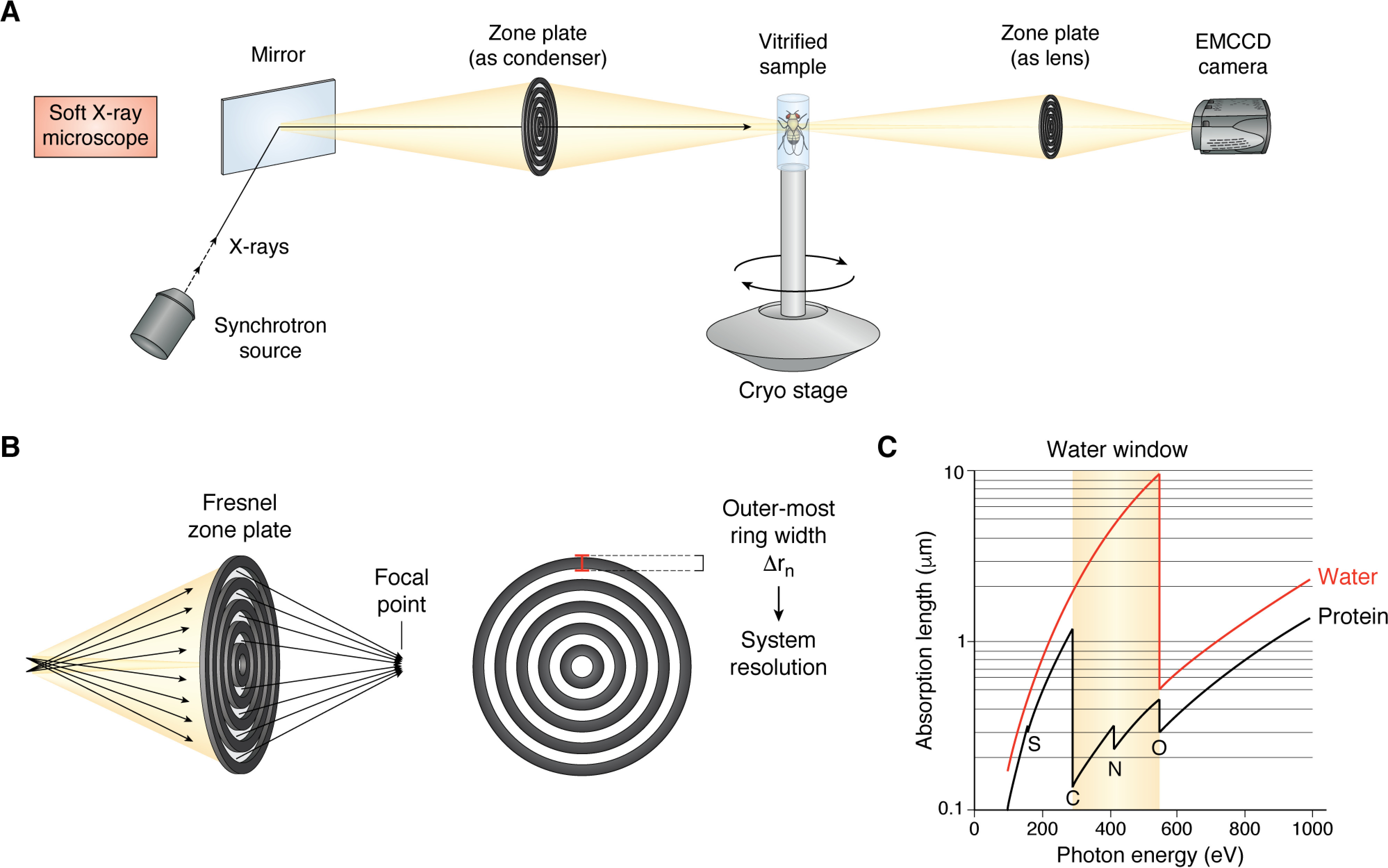
Soft X-ray microscope design and principle. A, diagrammatic representation of a soft X-ray microscope. X-rays from a synchrotron source are passed through a bend magnet and steered to the stage via a mirror. Fresnel zone plates are used as both the condenser and the lens. Vitrified samples are mounted on a cryo-stage, and images are collected directly on an EMCCD. B, a Fresnel zone plate consists of radially symmetric rings, with the outermost ring of the objective zone plate effectively determining the resolution of the system. C, K-absorption edges of carbon (284 eV) and oxygen (543 eV) form the “water window,” at which energies water (red trace) is transparent but protein (black trace) can generate sufficient contrast for imaging.
