Figure 3.
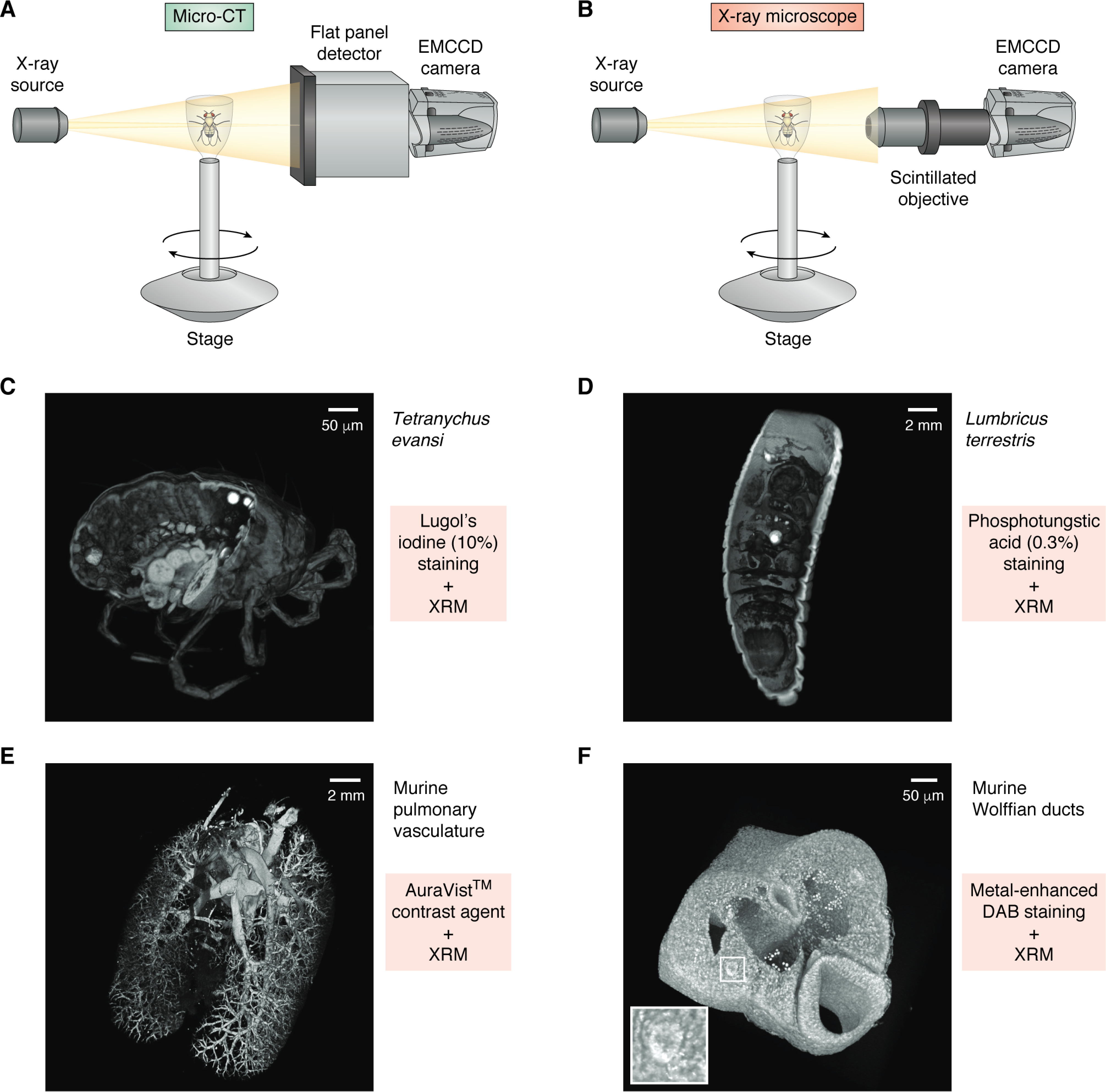
Micro-CT and X-ray microscope design and use of contrast agents. A, diagrammatic representation of a micro-CT system, comprised of an X-ray source and a flat panel detector coupled to an EMCCD camera. Samples are mounted to a rotating stage between the source and the detector. Magnification is solely dependent on geometric ratio of source to sample and sample to detector. B, an X-ray microscope is similar in design to a micro-CT but introduces a high-numerical aperture objective that utilizes a scintillator to detect X-rays and emit photons that are detected by the EMCCD. The objective adds a second magnification factor to an XRM system. C–F, examples of volume-rendered XRM tomograms of biological samples stained using different contrast agents (each tomogram is digitally cut to illustrate stain penetration). C, Tetranychus evansi, stained using 10% Lugol's iodine. D, Lumbricus terrestris, stained with 0.3% phosphotungstic acid. E, murine pulmonary vasculature filled with AuroVist™ contrast agent. F, metal-enhanced DAB staining of murine Wolffian ducts (white box and inset).
