Figure 5.
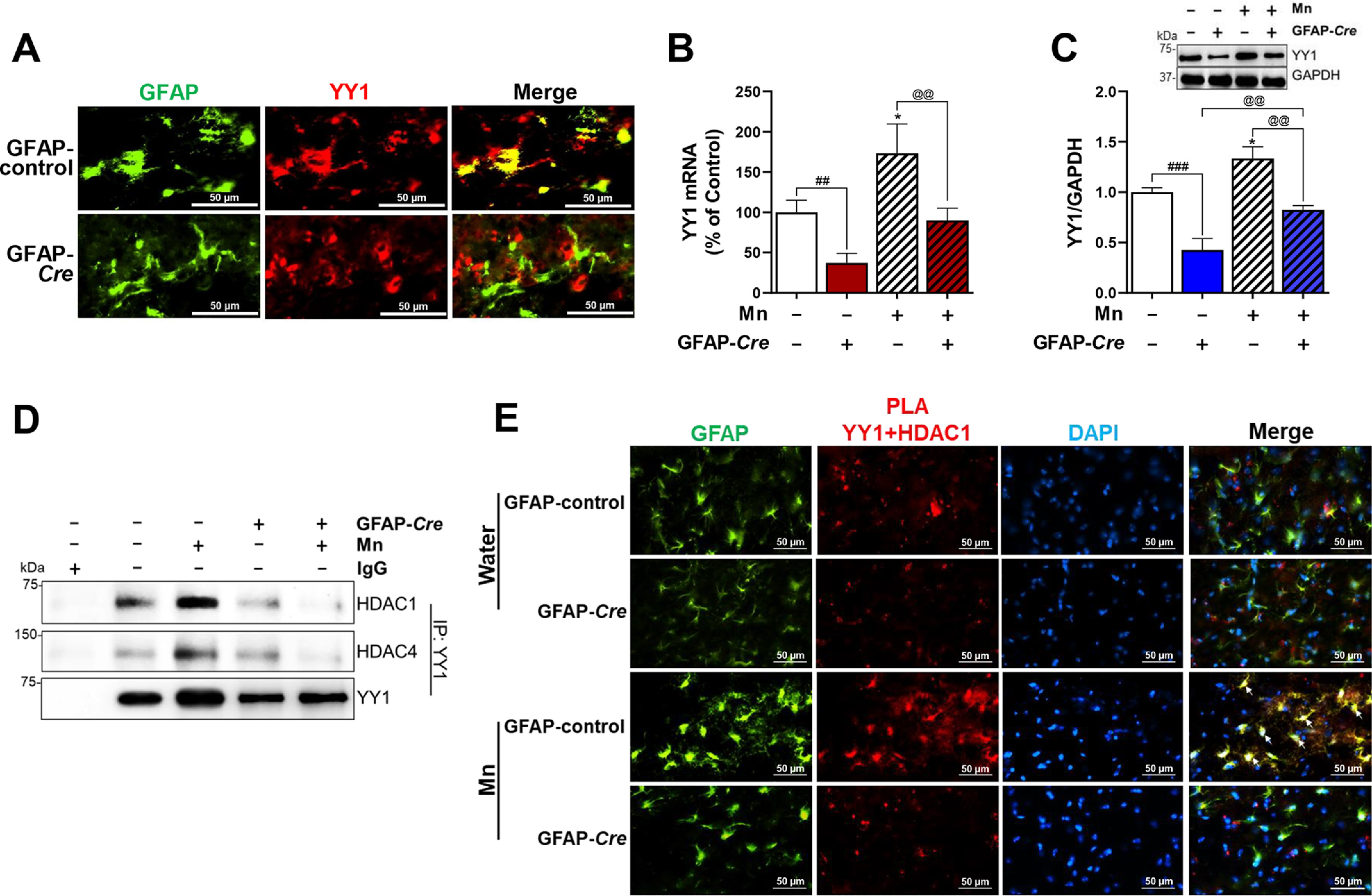
Astrocytic YY1 deletion by infusion of AAV-GFAP-Cre-GFP viral vectors into the SN attenuates Mn-increased YY1 expression and YY1 interaction with HDACs. A, after AAV infusion, coronal sections were stained with antibodies for GFAP and YY1, followed by IHC as described under “Experimental procedures.” Cells stained with GFAP (green) depict astrocytes and YY1 (red) indicates YY1 expression (×40 magnification). B and C, after Mn treatment, midbrain samples were extracted for total RNA and protein, followed by qPCR and Western blotting, as described under “Experimental procedures.” YY1 mRNA (B) and protein (C) levels in the midbrain were measured. GAPDH was used as loading controls of mRNA and protein. D, midbrain samples were tested for interaction of YY1 with HDAC1 and/or HDAC4 by co-IP as described under “Experimental procedures.” E, interaction of YY1 and HDAC1 in the SN of the mouse brain was determined by proximity ligation assay (×40 magnification). GFAP (green), YY1-HDAC1 proximity ligation signal (red), and DAPI (blue). *, p < 0.05 compared with the controls; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001; @@, p < 0.01 compared with each other (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test; n = 3). Data are expressed as mean ± S.D.
