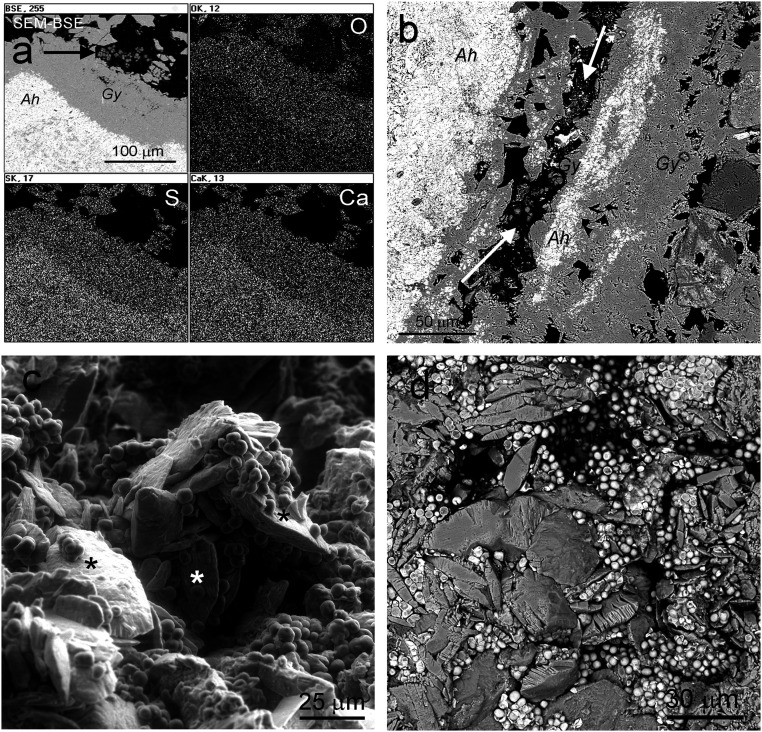
Fig. 1.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) maps from gypsum (Atacama Desert) colonized by endolithic microorganisms. (A) SEM in backscattered electron mode (SEM-BSE) contrast image of gypsum (Gy) and anhydrite (Ah) (Tarapacá region) and EDS distribution maps of oxygen, sulfur, and calcium, confirming the nature of these Ca sulfates; arrow, endoliths surrounded only by gypsum. (B) SEM-BSE contrast image of Gy and Ah (Tarapacá region); arrows, endoliths surrounded only by gypsum. (C) Environmental SEM image shows randomized attachment of cyanobacteria to the different gypsum planes; asterisks indicate {010} gypsum planes. (D) SEM-BSE image showing randomized oriented gypsum crystals surrounded by endolithic cyanobacteria, which are attached to all possible gypsum planes.