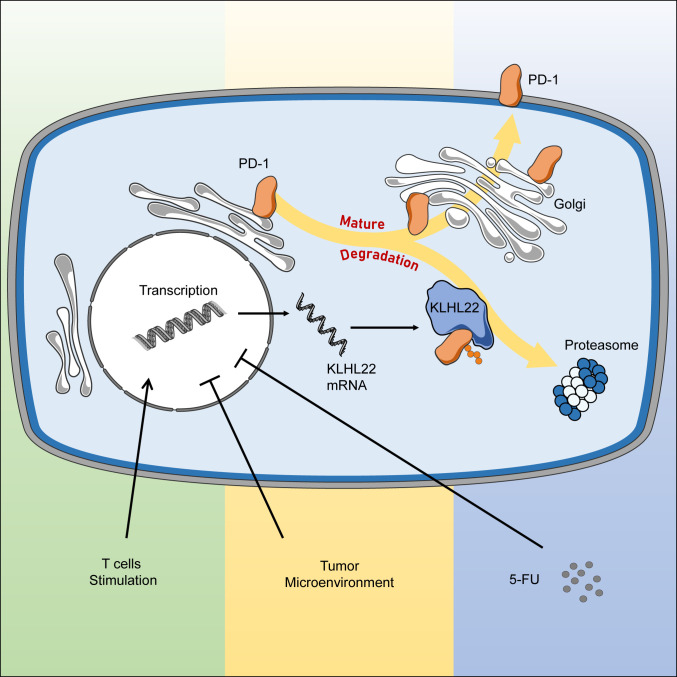
Fig. 8.
Working model. The biogenesis of PD-1 contains multiple steps of transportation and modification along the ER–Golgi–plasma membrane trafficking axis. KLHL22 is a major interacting protein of PD-1 and recognizes incompletely glycosylated PD-1, subsequently ubiquitinating and degrading PD-1 before it is transported to the cell surface. T cell activation upon TCR stimulation simultaneously promotes PD-1 and KLHL22 expression. KLHL22 degrades incompletely glycosylated PD-1 and maintains PD-1 homeostasis, preventing excessive suppression of T cells. KLHL22 deficiency, as well as deregulation of KLHL22 in response to the tumor microenvironment or 5-FU treatment, leads to excessive accumulation of PD-1 on the T cell surface and the repression of the antitumor immunity activity of T cells.