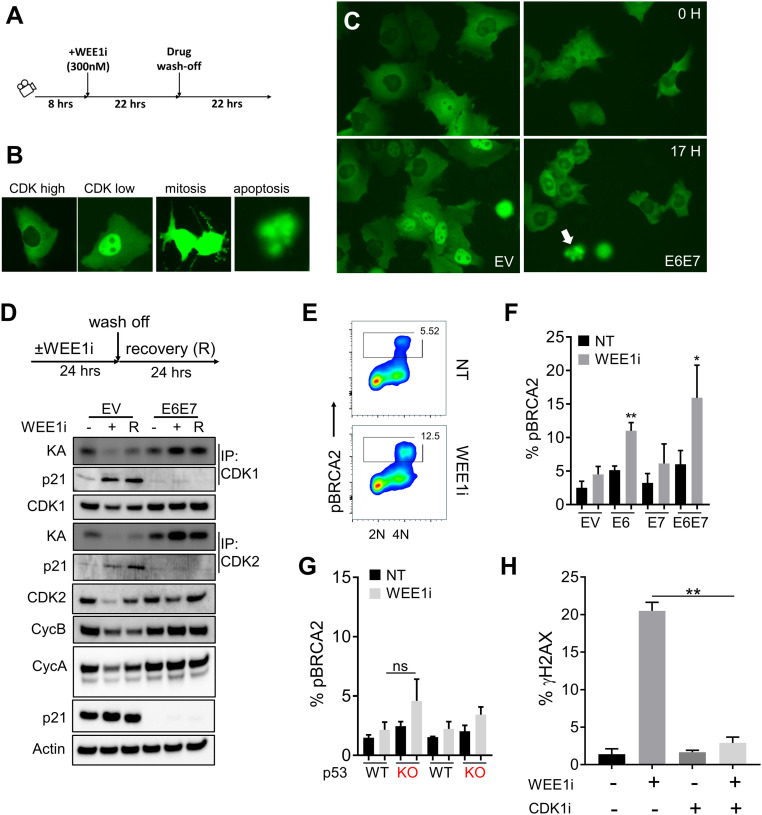
Fig. 3.
Aberrant CDK1 activation by WEE1i in E6 and E6/E7 cells is genotoxic. (A) Experimental design. DHB-mVenus CDK1/2 reporter in EV or E6/E7 cells treated as indicated was monitored by live cell imaging. (B) Examples of CDK high, CDK low, mitotic, and apoptotic cells are shown. (C) Examples of EV and E6/E7 cells expressing CDK1/2 reporter after exposure to WEE1i as indicated. Pairs of images of each cell type represent the same field taken 17 h apart. Note high nuclear signal (low CDK1/2) in EV cells at 17 h of WEE1i vs. low nuclear signal (high CDK1/2) in E6/E7 cells. White arrow indicates apoptotic cell morphology. (D) CDK1/2 kinase activity (KA) was measured by in vitro kinase assays of immunoprecipitated (IP) cyclin/CDK complexes as indicated. EV and E6/E7 cells were treated ± WEE1i and released as indicated. Protein extracts were isolated and analyzed for protein abundance and kinase activity. (E) FACS analysis of CDK1-mediated pBRCA2 (serine 3291) in WEE1i-treated E6/E7 (predominantly G2/M) cells. (F) Percentages of pBRCA2+ cells analyzed by FACS in EV, E6, E7, and E6/E7 cells ± WEE1i (n = 2). (G) Percentages of pBRCA2+ cells in p53 +/+ and p53 −/− UM-SCC74a cells ± WEE1i; ns, not signficant. (H) Percentages of γH2AX analyzed by FACS in UM-SCC74a E6/E7 cells treated ± WEE1i and/or CDK1i as indicated for 3 h (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.