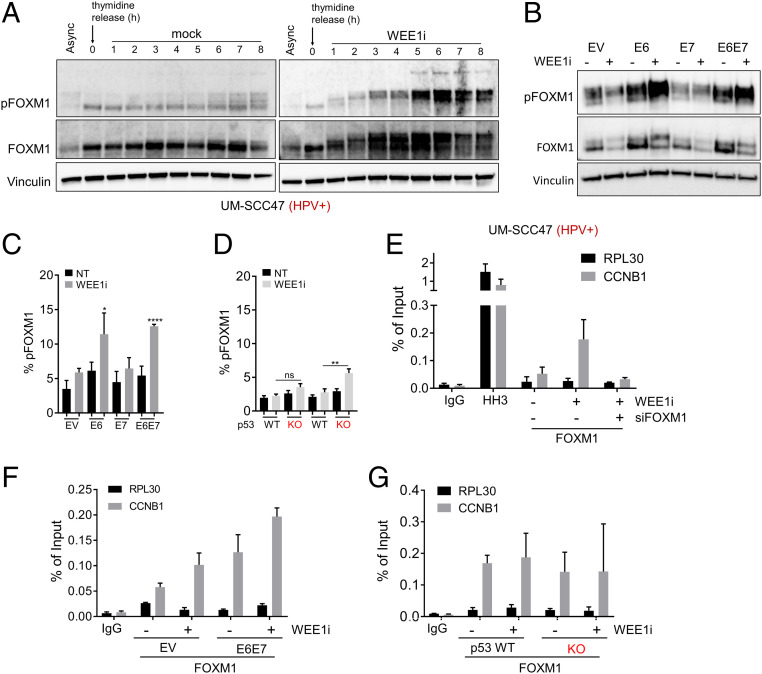
Fig. 4.
Hyperactivation of FOXM1 mitotic switch by WEE1i in HPV+ cells via E6/E7. (A) Western blots of UM-SCC47 cell lysates. Cells were synchronized in thymidine for 24 h then released into fresh media ± WEE1i as indicated. (B) Western blots of asynchronous EV, E6, E7, and E6/E7 UM-SCC74a cell lysates ± WEE1i. (C) FACS analysis of FOXM1-phosphothreonine 600 (pFOXM1) in EV, E6, E7, and E6/E7 ± WEE1i. (D) FACS analysis of pFOXM1 in p53−/− vs. p53+/+ clones ± WEE1i. (E) ChIP-qPCR of FOXM1 at CCNB1 promoter in WEE1i-treated UM-SCC47 cells. Enrichment of FOXM1 is absent in FOXM1-depleted cells. No enrichment at RPL30 promoter (negative control). (F) ChIP-qPCR of FOXM1 at CCNB1 promoter in EV vs. E6/E7 UM-SCC74a E6/E7 cells ± WEE1i. Data are shown as fold increase relative to untreated EV cells. (G) ChIP-qPCR of FOXM1 at CCNB1 promoter in p53+/+ and p53 −/− UM-SCC74a cells. Data are shown as fold increase relative to untreated p53+/+ cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.00001.