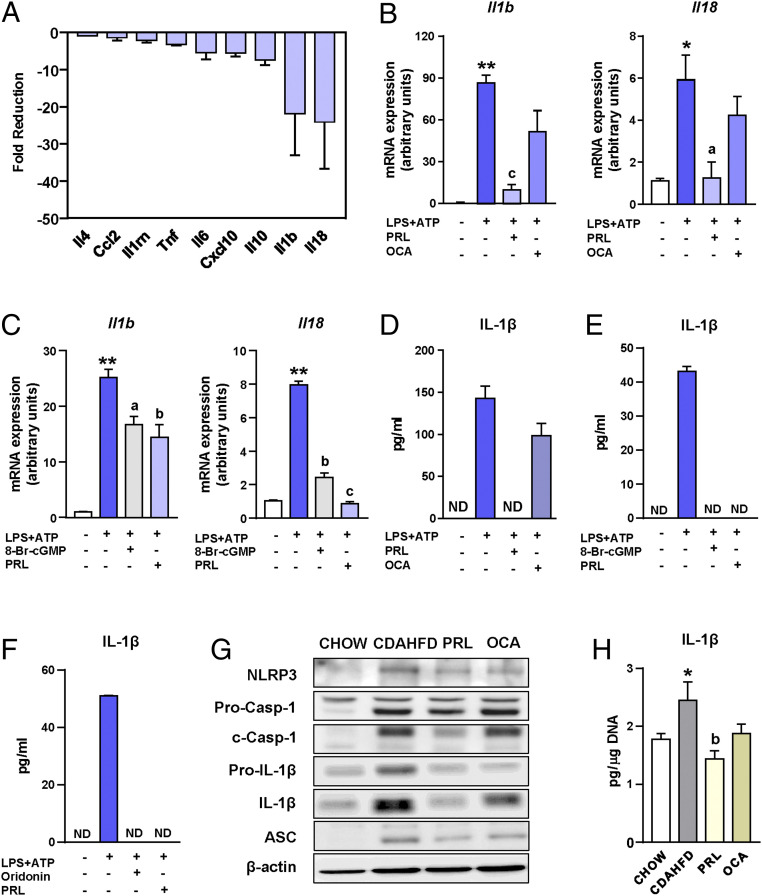
Fig. 4.
Antiinflammatory actions of PRL are associated with inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome. (A) Fold reduction in the expression of inflammatory genes induced by the addition of PRL to incubations of Kupffer cells exposed to LPS. (B) Il1b and Il18 mRNA expression in isolated Kupffer cells challenged with LPS + ATP and treated with PRL or OCA. (C) Il1b and Il18 mRNA expression in isolated Kupffer cells challenged with LPS + ATP and treated with PRL or the cGMP analog 8-Br-cGMP. (D) IL-1β levels in supernatants of Kupffer cells from B as determined by ELISA. (E) IL-1β levels in supernatants of Kupffer cells from C. (F) IL-1β levels in supernatants of Kupffer cells challenged with LPS + ATP and treated with PRL or the NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor oridonin. (G) NLRP3, pro-caspase-1, cleaved-caspase-1, pro-IL-1β, IL-1β, ASC, and β-actin protein levels in liver tissue from the mice included in the four groups of the study as determined by SDS/PAGE Western blot. (H) IL-1β levels in the liver relative to the DNA content. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of n = 4 separate experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 vs. chow or vehicle; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005, and cP < 0.001 vs. CDAHFD or LPS + ATP. ND, not detectable.