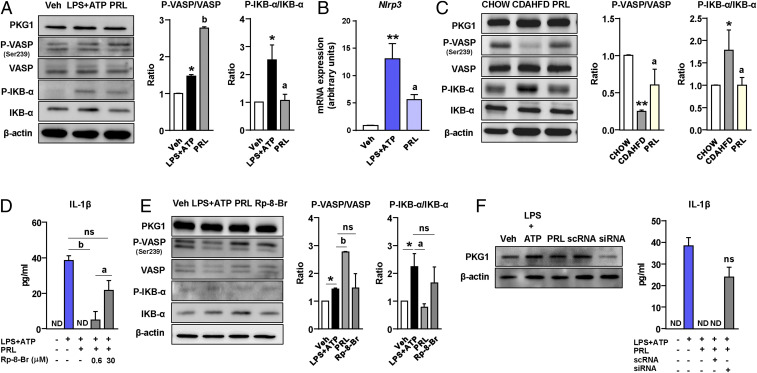
Fig. 5.
PRL blocks the NLRP3 inflammasome in Kupffer cells through mechanisms based on VASP phosphorylation and NF-κB inhibition. (A, Left) PKG1, phospho-VASP (Ser239) (P-VASP), VASP, phospho-IKB-α (P-IKB-α), IKB-α, and β-actin protein levels in Kupffer cells challenged with LPS + ATP alone or in the presence of PRL. (A, Right) Densitometric analysis of the P-VASP/VASP and P-IKB-α/IKB-α ratios. (B) Nlrp3 mRNA expression in Kupffer cells incubated in the conditions described in A. (C, Left) PKG1, P-VASP (Ser239), VASP, P-IKB-α, IKB-α, and β-actin protein levels in liver tissue from the mice included in the four groups of the study. (C, Right) Densitometric analysis of the P-VASP/VASP and P-IKB-α/IKB-α ratios. (D) Levels of mature IL-1β in supernatants from Kupffer cells challenged with LPS + ATP and treated with PRL in the presence or absence of the PKG-blocking agent Rp-8-Br at 0.6 and 30 μM concentrations. (E, Left) PKG1, P-VASP (Ser239), VASP, P-IKB-α, IKB-α ,and β-actin protein levels in Kupffer cells challenged with LPS + ATP and treated with PRL in the presence or absence of Rp-8-Br. (E, Right) Densitometric analysis of the P-VASP/VASP and P-IKB-α/IKB-α ratios. (F, Left) PKG1 and β-actin protein levels in Kupffer cells incubated with vehicle (Veh) and LPS + ATP alone or in combination with PRL, PRL plus scrambled nontargeting RNA (scRNA), and PRL plus siRNA targeting the Prkg1 gene. (F, Right) IL-1β levels in supernatants of Kupffer cells incubated under these conditions. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM of n = 3 or 4 separate experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 vs. chow or vehicle; aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.005 vs. CDAHFD or LPS + ATP. ns, not statistically significant vs. LPS + ATP.