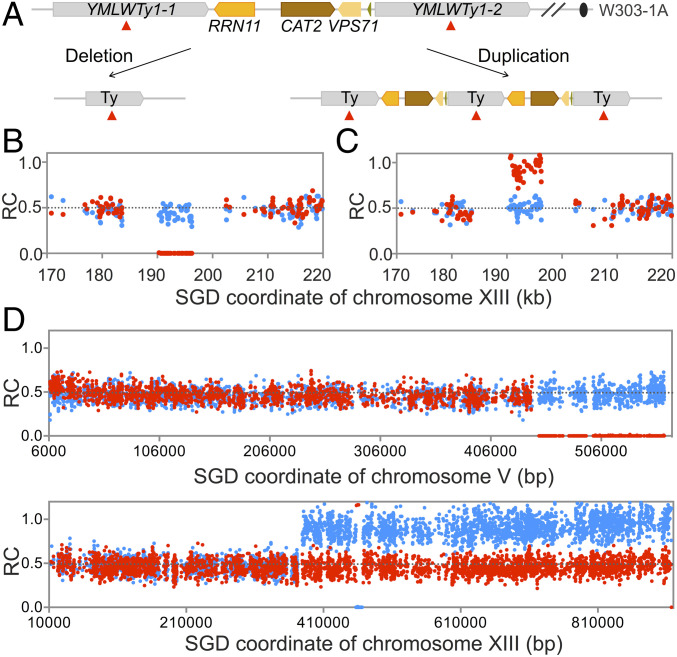
Fig. 2.
Patterns of deletions and duplications resulting from recombination between nontandem repeats. (A) Chromosomal region that is a hotspot for deletions and duplications on chromosome XIII. Both deletions and duplications are a consequence of homologous recombination between YMLWTy1-1 and YMLWTy1-2. (B) Heterozygous deletion between YMLWTy1-1 and YMLWTy1-2. Red and blue dots reflect the number of “reads” of W303-specific and YJM789-specific SNPs, respectively. The number of reads of W303-specific and YJM789-specific SNPs are divided by the average number of W303-specific plus the YJM789-specific reads for all SNPs in the genome, resulting in the RC (ratio of coverage) of W303-specific and YJM789-specific SNPs. Thus, SNPs represented in zero, one, or two copies in the genome have RC values of about 0, about 0.5, and about 1, respectively. The deleted region corresponds to the region containing the RRN11, CAT2, and VSP71 genes on the W303-derived chromosome. (C) Heterozygous duplication between YMLWTy1-1 and YMLWTy1-2. (D) Terminal deletion on chromosome V and terminal duplication on chromosome XIII in isolate Spo11-188. The breakpoint of the deletion is at YERCTy1-1, and the duplication breakpoint is at YMRCTy1-4. As shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S1 B and C, pairs of terminal deletions and duplications likely reflect translocations formed by recombination between repeats on nonhomologous chromosomes. This translocation was confirmed by other methods as described in the text.