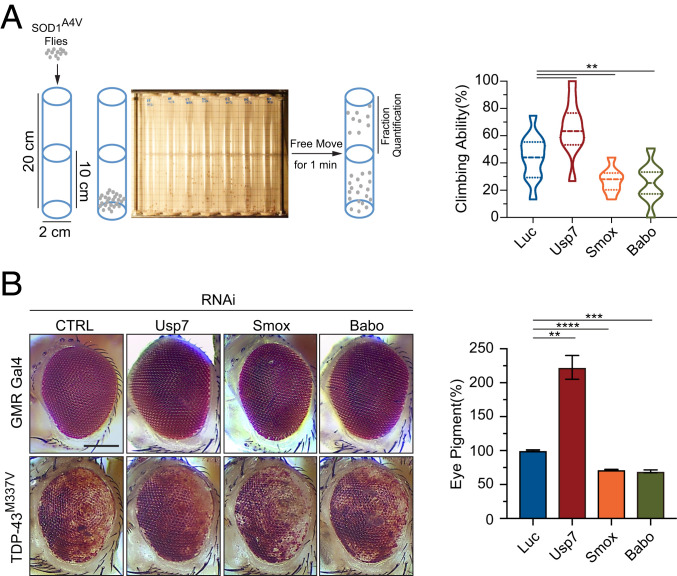
Fig. 6.
The knockdown of Drosophila Usp7 suppresses neurotoxicity induced by mutant SOD1 or TDP-43. (A) Chart of the climbing (negative geotaxis) assay in adult Drosophila expressing human SOD1A4V in motor neurons (Left). Quantification of the climbing ability of Drosophila expressing human SOD1A4V in motor neurons, together with gene-specific RNAi against Usp7 (34708), Smox (26756), Babo (40866), or control RNAi (Right; n = 8 independent groups; **P < 0.01). (B) Reduction in Usp7 by RNAi (34708) strongly suppresses the eye degeneration phenotypes in TDP-43M337V strains, while reduction in Smox (RNAi 26756) or Babo (RNAi 40866) worsens the eye degeneration phenotypes, when compared with the control Luc RNAi strain (Left). (Scale bar, 100 μm.) Quantification of pigment content in adult eyes confirms the protection against degeneration by a loss of Usp7 in TDP-43M337V strains (Right). The measurements represent three independent groups, each containing fly heads from two males and two females (n = 3; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Error bars indicate ± SEM.