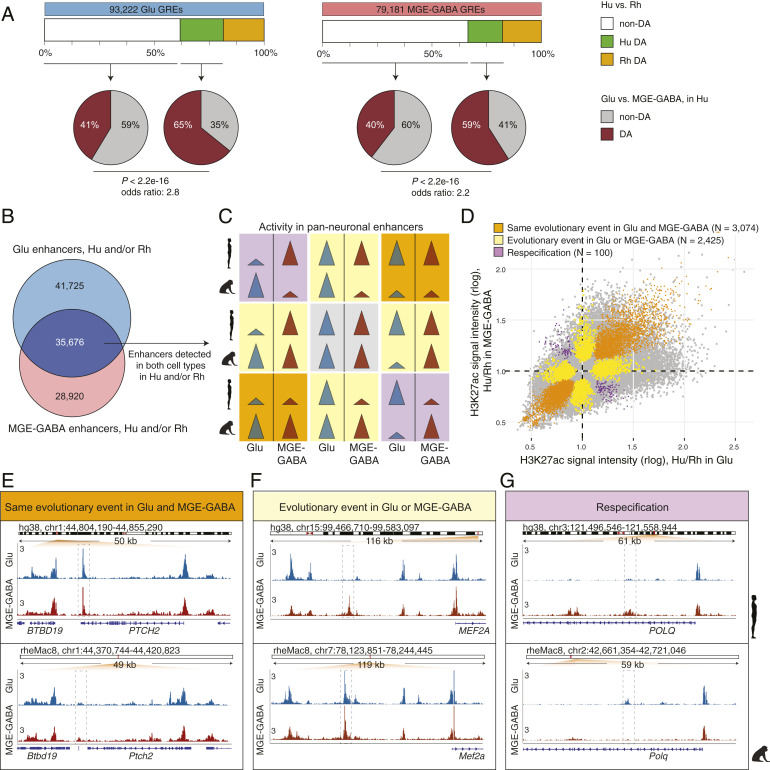
Fig. 2.
Evolutionary changes in neuron subtype-specific and pan-neuronal regulatory elements. (A) Cell type specificity of Hu > Rh DA (green boxes) or non-DA (white boxes) GREs. GREs detected in Glu (Left) or MGE-GABA (Right) neurons in Hu and/or Rh. Pie charts indicate fractions of DA (brown) or non-DA (gray) GREs between neuronal subtypes in Hu. In both neuronal subtypes, Hu > Rh DA GREs were more often neuron-subtype-specific than non-DA GREs (P < 2.2e-16; Fisher’s exact test). (B) Venn diagram of the overlap between Glu and MGE-GABA enhancers in Hu and/or Rh. The overlapping enhancers (dark blue) are positionally shared in Glu and MGE-GABA neurons (pan-neuronal). (C) Schematic of possible evolutionary changes in pan-neuronal enhancers in Hu and/or Rh. Gray, no evolutionary change in any neuronal subtype; orange, same direction of an evolutionary change in both subtypes; yellow, an evolutionary change in only one subtype; purple, different direction of an evolutionary change between subtypes (respecification). (D) Simultaneous cross-species and cross-cell–type analysis of H3K27ac signal intensities for pan-neuronal enhancers in Hu and/or Rh (Methods and SI Appendix, Fig. S2C). Shown are DA GREs confirmed by the analysis to undergo the type of an evolutionary change described in C. (E–G) Examples of enhancers (dashed boxes) with the same direction of evolutionary change in Glu and MGE-GABA (E, the PTCH2 locus), with an evolutionary change in only one neuronal subtype, MGE-GABA (F, near MEF2A), and with evolutionary changes in opposite directions in Glu and MGE-GABA neurons (respecification) (G, the POLQ locus).