FIGURE 5.
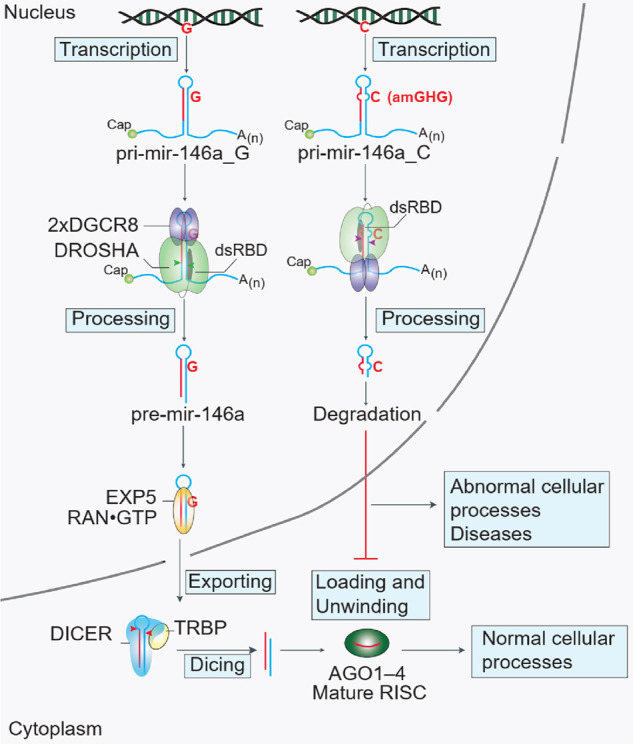
Schematic representation of a hypothetical model to explain how the G/C SNP (rs2910164) reduces the expression of miR-146a. The G and C alleles located in the 5q33 locus of chromosome 5 are different in one nucleotide. These two alleles are transcribed into two different pri-mir-146a molecules. Pri-mir-146a_C has a strong amGHG motif, which interacts with the dsRBD of DROSHA, and in this way, it efficiently recruits DROSHA to the apical junction. Therefore, the Microprocessor cleaves pri-mir-146a_C more at the unproductive sites, generating a short hairpin, which is an unproductive product. This unproductive product does not produce miR-146a, and it might be degraded in human cells. As pri-mir-146a_G is cleaved more at the productive sites, it generates more pre-mir-146a, which is in turn passed through the DICER and Ago steps to become mature miR-146a. RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex.
