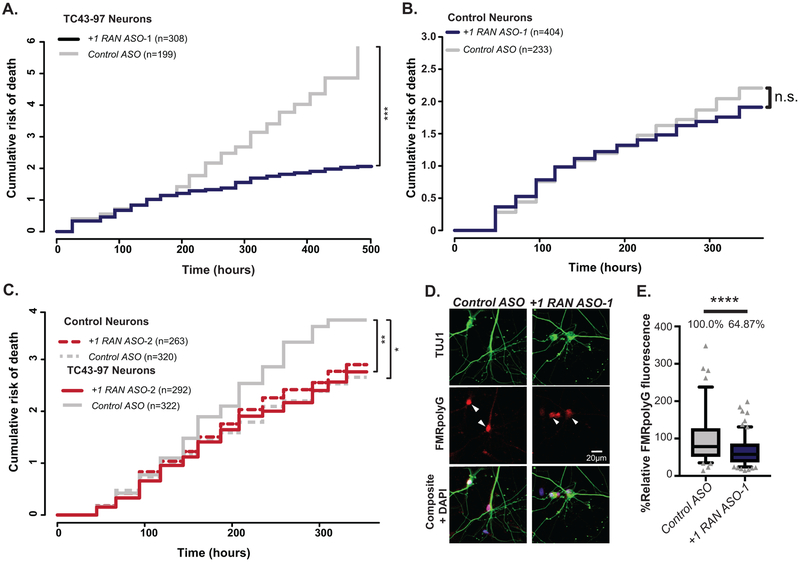
Figure 6: CGG RAN ASO enhances survival in expanded repeat human neurons.
A) Survival analysis in TC43–97 human neurons treated with 150nM +1RAN ASO-1 (n=308) or Control ASO (n=199) (p<0.001). B) Survival analysis in control human neurons treated with 150nM +1RAN ASO-1 (n=404) or Control ASO (n=233) (p=0.709). C) Survival analysis in TC43–97 (n=292, 322) and control (n=263, 320) human neurons treated with 150nM +1RAN ASO-2 or Control ASO, respectively (Control/Control ASO vs TC43–97/Control ASO: p=0.0105, TC43–97/Control ASO vs TC43=97/+1RAN ASO-2: p=0.0015). D) Immunocytochemistry to FMRpolyG (red) in mature TC43–97 neurons (TUJ1-positive (green)) treated with +1RAN ASO-1 or Control ASO treatment. E) Quantification of FMRpolyG signal (corrected total cellular fluorescence) in TC43–97 neurons treated with +1RAN ASO-1 (n=194) or Control ASO (n=93), where “n” is the mean CTCF signal from 5 neurons (p<0.001). Panel A, B, C: Cox proportional hazard analysis. Survival is plotted as cumulative risk of death. Panel E: Two sided Mann Whitney U test. Box in graph extends to the 25th and 75th percentiles of data points with a line at the mean, and whiskers indicate 95% confidence interval. n.s.=not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.