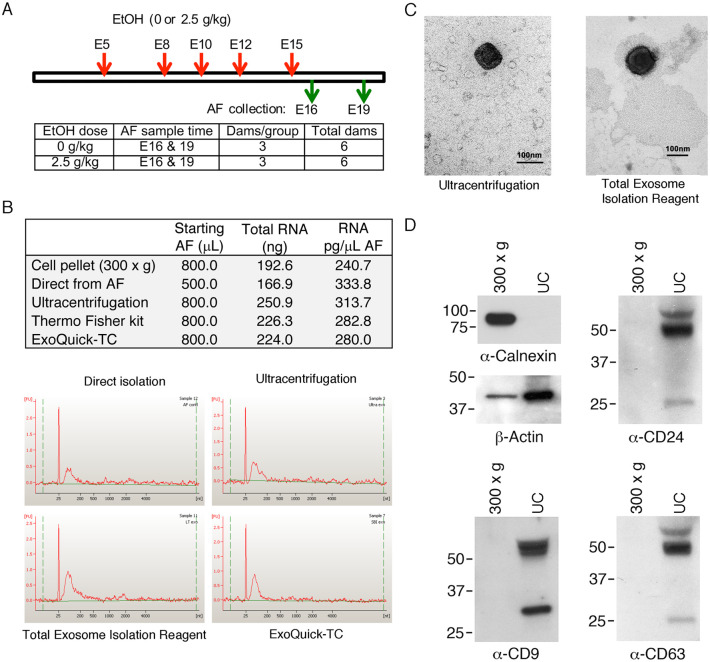
Fig 1. Isolation and characterization of amniotic fluid exosomes from rat fetal alcohol exposure (FAE) model.
(A) Rat FAE model schematic. Timed pregnant rats were treated with water or 2.5 g/kg of 20% EtOH by oral gavage at E5, 8, 10, 12 and 15. Animals were euthanized at E16 or E19 for embryo collection (n = 3 each). (B) Comparison of amniotic exosome and exosomal RNA isolation by ultracentrifugation and two commercial kits (Total Exosome Isolation Reagent from Thermo Fisher and ExoQuick-TC from SBI). Cell pellet (300 x g) fraction and RNA isolation by direct lysis of AF are included for comparison. Graphs shown at the bottom are Bioanalyzer profiles of extracted exosomal RNA using a Nano kit. (C) Electron microscopic examination of amniotic exosomes purified by ultracentrifugation and Total Exosome Isolation Reagent (Thermo Fisher) (bar = 100 nm). (D) Immunochemical assessment of exosome purification by staining exosomal proteins with anti-Calnexin (endoplasmic marker), anti-Actin and exosomal markers (anti-CD9, CD24 and CD63). The level of the markers in the cell pellet (300 x g) fraction and ultracentrifugation fraction (UC) was compared.