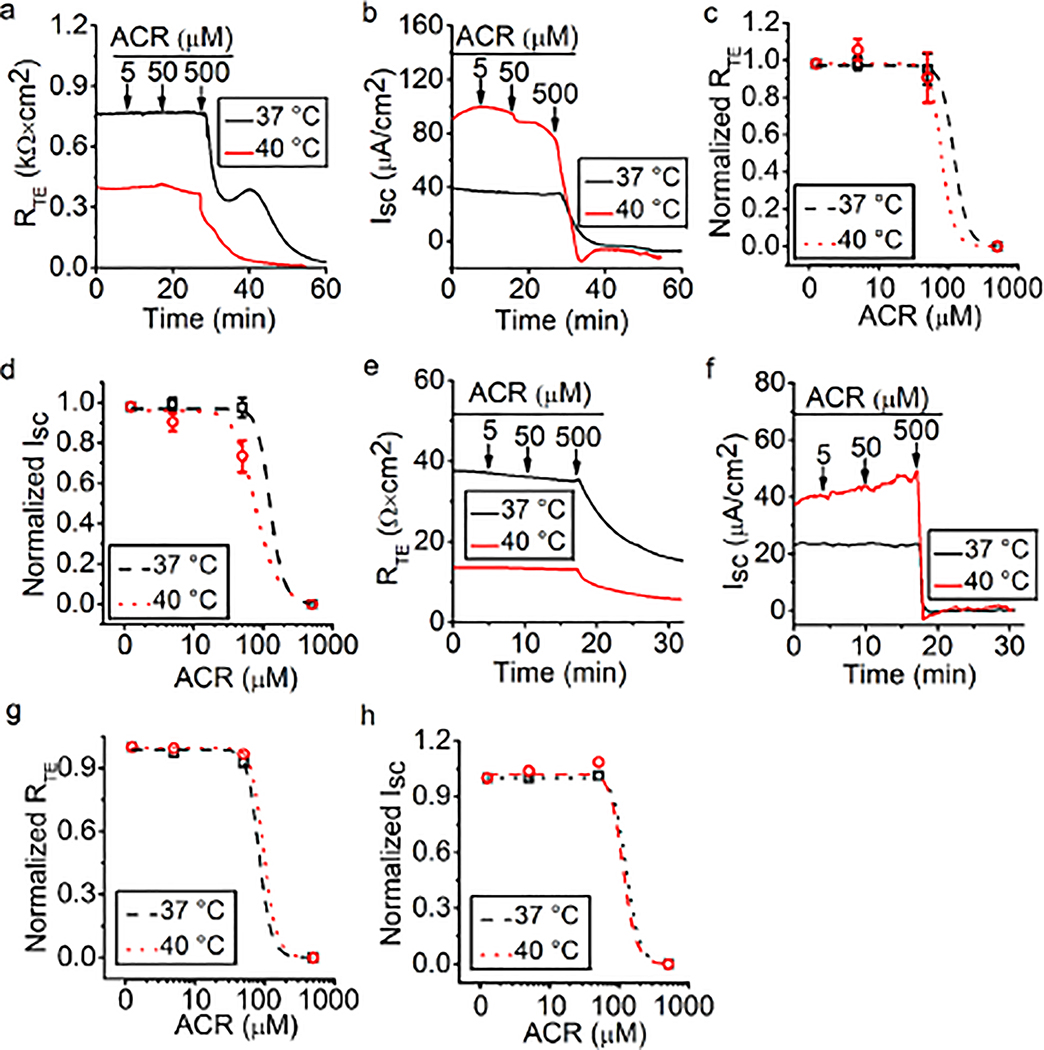
Fig. 5.
Acrolein impairs bioelectric features in MTE and HBE monolayers. (a, b) Representative RTE and ISC traces in the presence of 5, 50, and 500 μM acrolein at 37°C (black lines) and 40°C (red lines) in MTE monolayers. Acrolein (ACR, 5, 50, and 500 μM) was pipetted to the bath as indicated by arrows. 500 μM acrolein decreased RTE and ISC. (c, d) Dose-response curve for acrolein in MTE monolayers. Normalized RTE/ISC points were fitted with the Hill equation (START = 1, END = 0, n = 22). The Ki value of RTE for acrolein was 120.22 μM at 37°C and 79.43 μM at 40°C; The Ki value of ISC for acrolein was 125.89 μM at 37°C and 77.62 μM at 40°C. (e, f) Representative RTE and ISC traces of HBE monolayers in the presence of 5, 50, and 500 μM acrolein under conditions of 37°C (black line) and 40°C (red line). Arrows indicated the time to add acrolein (ACR, 5, 50, and 500 μM). RTE and ISC were decreased by 500 μM acrolein. (g, h) Dose-response curve for acrolein in HBE monolayers. Normalized RTE/ISC points were fitted by the Hill equation (START = 1, END = 0, n = 2). The Ki value of RTE for acrolein was 83.18 μM at 37°C and 97.73 μM at 40°C, respectively; the Ki value of ISC for acrolein was 125.89 μM at 37°C and 112.21 μM at 40°C, respectively.