Figure 4. Nuclear receptor (NR) signaling in osteoclasts.
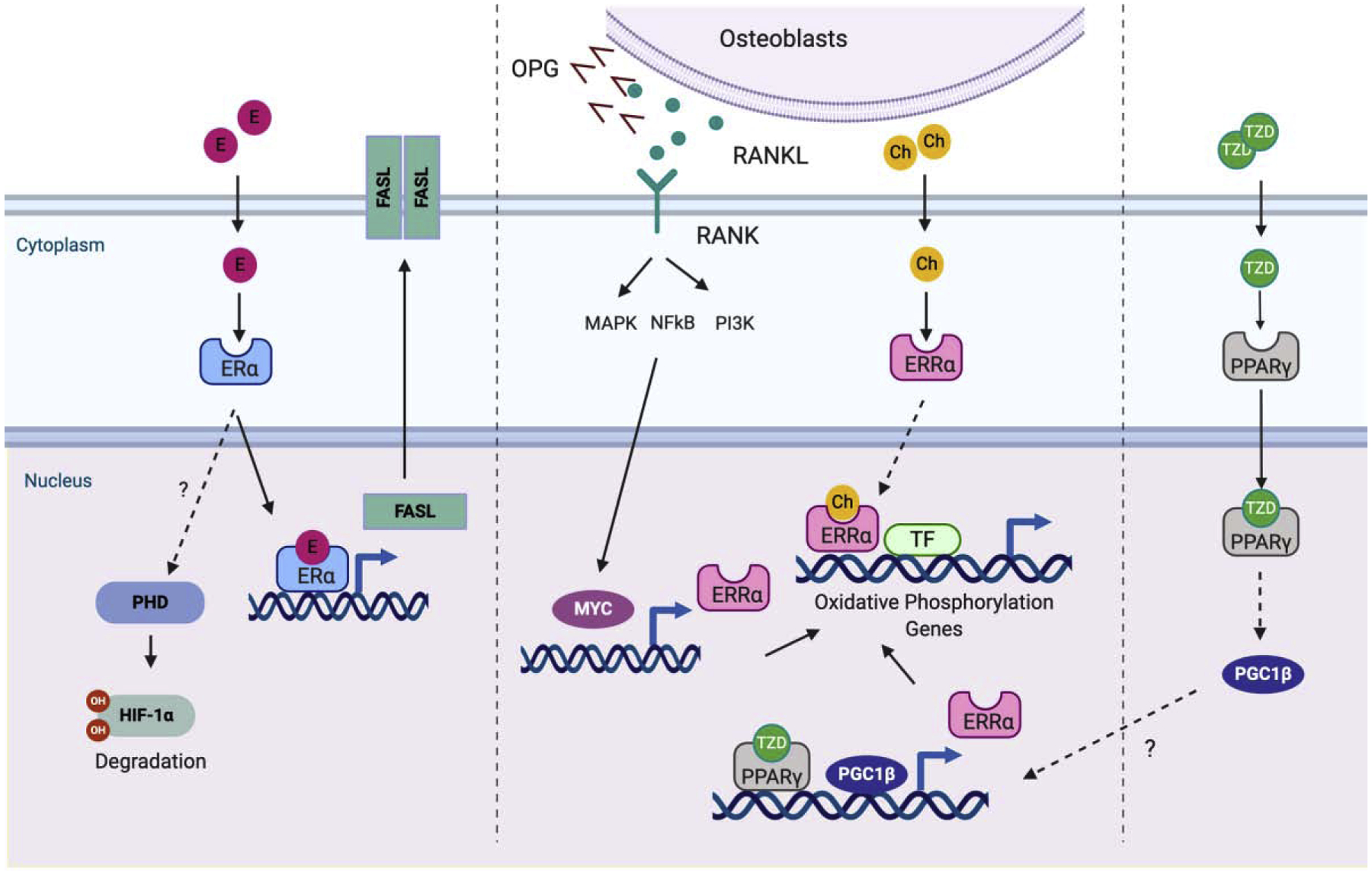
On binding of RANKL to RANK, MYC is induced. MYC binds to the promoter of ERRα to induce the expression of ERRα. ERRα subsequently activates genes related to oxidative phosphorylation which is a key metabolic mechanism of osteoclast differentiation. The MYC-ERRα axis plays an important role in osteoclast differentiation. The thiazolidinedione (TZD) family binds to and activates PPARγ. PPARγ indirectly induces PGC1β. Both PPARγ and PGC1β bind to the promoter of ERRα. Estrogen negatively regulates osteoclastogenesis. Estrogen binds to and activates ERα. Activated ERα induces HIF1α degradation and FASL expression to enhance apoptosis of osteoclasts. Osteoblasts/osteocytes secrete OPG and RANKL. The activation of NRs in osteoblasts regulates the ratio of RANKL to OPG to modify RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. factors to initiate the osteoclastogenenic program. Then committed cells (osteoclast precursor cells) fuse to each other and generate multinucleated
