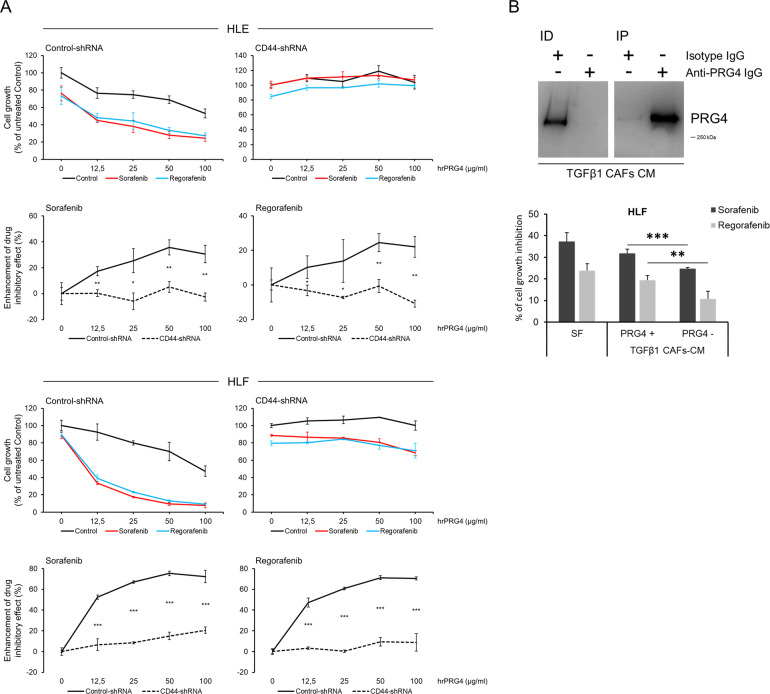
Fig. 6. CD44 silencing in HCC cells offsets the enhancement of drug effectiveness induced by rhPRG4.
a Cells were transduced via lentiviral infection and further selected for stable CD44-silencing. A 72-hour proliferation test was performed and the effect of increasing rhPRG4 concentrations (0–100 µg/ml) in enhancing the inhibitory action of sorafenib or regorafenib at a fixed concentration (2.5 µM) was plotted both for Control- and CD44-shRNA cells. The synergistic effect (enhancement of drug inhibitory effect) of combined drug + rhPRG4 is calculated for each rhPRG4 concentration as the percentage of cell growth inhibition by drug + PRG4, net of the effect of drug tested individually, with reference to control (rhPRG4 alone). b HCC CAFs were stimulated for 48 hours with TGFβ1 and further incubated for 48 hours (without TGFβ1) in serum-free conditions to allow enrichment of the conditioned medium (CM). The CM was then concentrated and PRG4-depleted or not. Western blot showing PRG4 depletion from CM of TGFβ1-treated CAFs. ID = immunodepleted TGFβ1-treated CAFs-CM using isotype or anti- PRG4 antibody; IP = immunoprecipitated PRG4 from TGFβ1-treated CAFs-CM using isotype or anti-PRG4 antibody. Whole blot scan is shown in Supplementary Fig. 5B. b Effect of TGFβ1-treated CAFs-CM PRG4 depleted/not depleted on sorafenib and regorafenib inhibitory action against HLF cell proliferation; 20 µg/ml of CM proteins were used in a 72-hour growth test in the presence of 1% FBS. Data are the means ± SD of triplicates. T test (unpaired, two-tailed): *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.