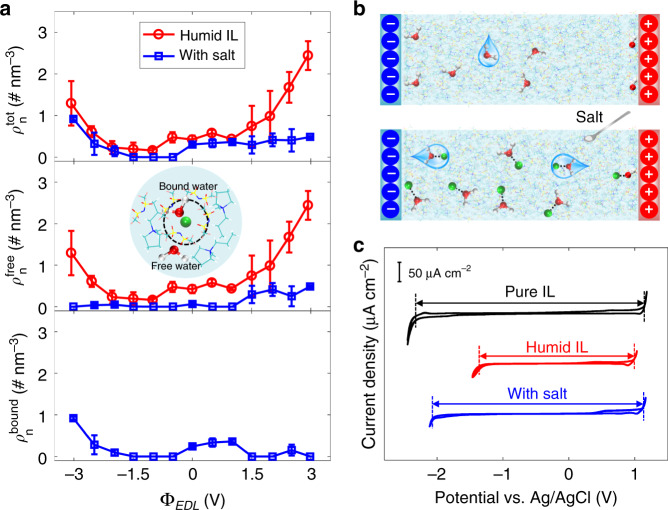
Fig. 2. Effect of adding salt on the interfacial water and electrochemical window of electrolytes.
a Electrosorption of water from humid 1-methyl-1-propylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ([Pyr13][TFSI]) with/without adding salt. The top, middle and bottom panels are, respectively, the number densities of the total (), free () and Li+-bound water () in the interfacial region. b Schematic of the effect of adding salt on water electrosorption. c Cyclic voltammograms of HOPG in pure [Pyr13][TFSI] (black line), humid [Pyr13][TFSI] (red line), and salt-in-humid [Pyr13][TFSI] electrolyte (the molar salt–water ratio = 1:1, blue line). Scan rate: 100 mV s−1. Water contents for humid [Pyr13][TFSI] are 4392 and 4474 ppm for MD simulation and cyclic voltammetry experiments, respectively.