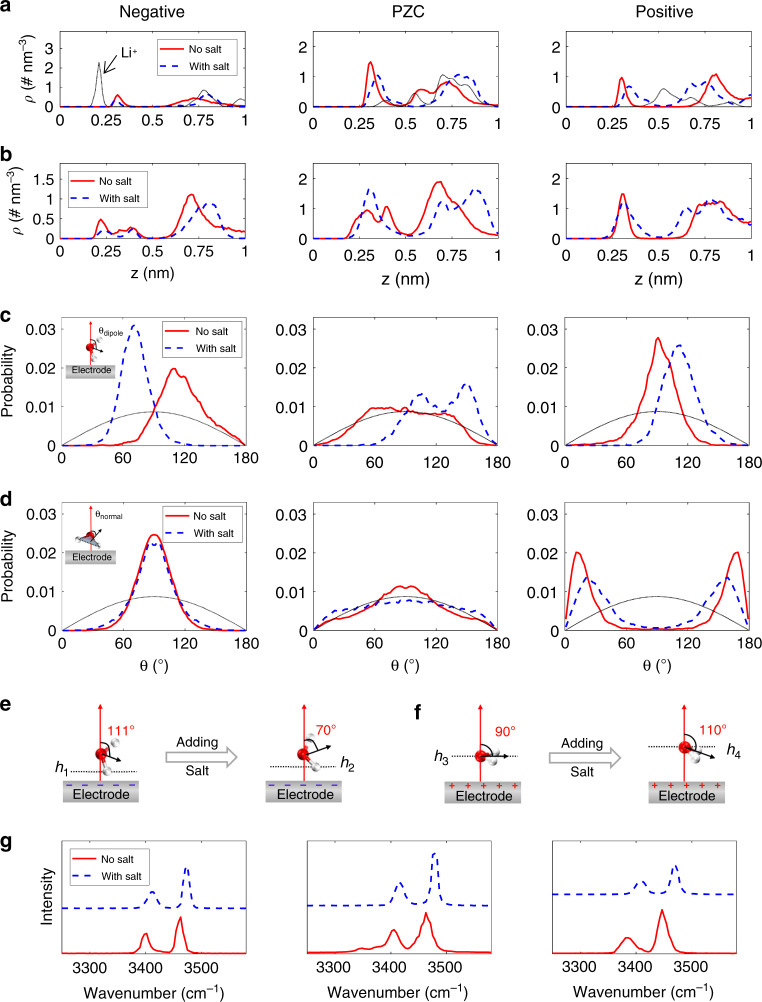
Fig. 5. Effect of adding salt on the structure of interfacial water in humid ionic liquids.
a The oxygen atom number densities (ρ) of water in humid ionic liquid (IL) (red solid line), and in salt-in-humid IL (blue dash line) at electrodes. The black dotted line is the atom number density of Li+ in salt-in-humid IL. b The hydrogen atom number densities of water in humid IL and in salt-in-humid IL at electrodes. c, d The dipole (c) and normal (d) orientations of interfacial water in humid IL (red solid lines) and in salt-in-humid IL (blue dash lines) at electrodes. θdipole is defined as the angle between the normal of the electrode surface and the water vector, and θnormal is the angle formed between the normal of the electrode surface and the normal of water plane. The black dotted line represents the orientation of bulk water. e, f Schematics of arrangement change of interfacial water under negative (e) and positive (f) polarizations in humid IL due to adding salt. g Infrared spectroscopy (IR) spectra of interfacial water in humid IL and in salt-in-humid IL. The electrical double-layer (EDL) potentials are −2 V and 1 V for negative and positive electrodes, respectively.