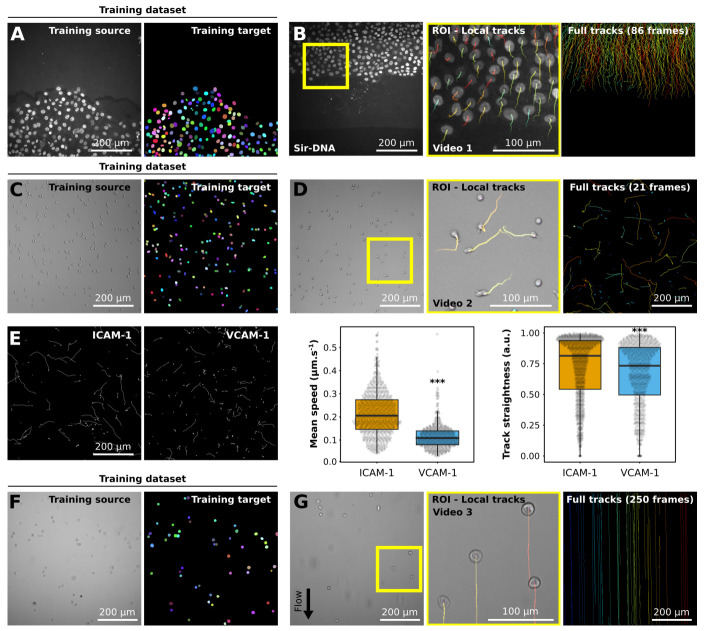
Figure 2. Example of datasets analyzed using StarDist and TrackMate.
( A, B) Migration of MCF10DCIS.com, labeled with Sir-DNA, recorded using a spinning disk confocal microscope and automatically tracked. Examples of images used to train StarDist ( A), and an example of results obtained using automated tracking are displayed ( B, Video 1). The yellow square indicates a magnified ROI, where the local track of each nucleus is displayed. The full cell tracks are displayed on the left. Tracks are color-coded as a function of their maximum instantaneous velocity (blue slow, red fast tracks). ( C– E) Migration of activated T cell plated on VCAM-1 or ICAM-1, recorded using a brightfield microscope and automatically tracked. Examples of images used to train StarDist ( C) and an example of results obtained using automated tracking are displayed ( D, Video 2). ( E) Comparison of the migration of activated T cells on VCAM-1 or ICAM-1. Track mean speed and track straightness were quantified. Data are displayed as boxplots. *** p-value = <0.001, p-values were determined using a randomization test. ( F, G) Cancer cells flowing in a microfluidic chamber, recorded live using a brightfield microscope and automatically tracked (Video 3). Examples of images used to train StarDist ( F), and an example of results obtained using automated tracking are displayed ( G). The full tracks shown here were color-coded as a function of their x coordinate.