FIGURE 2.
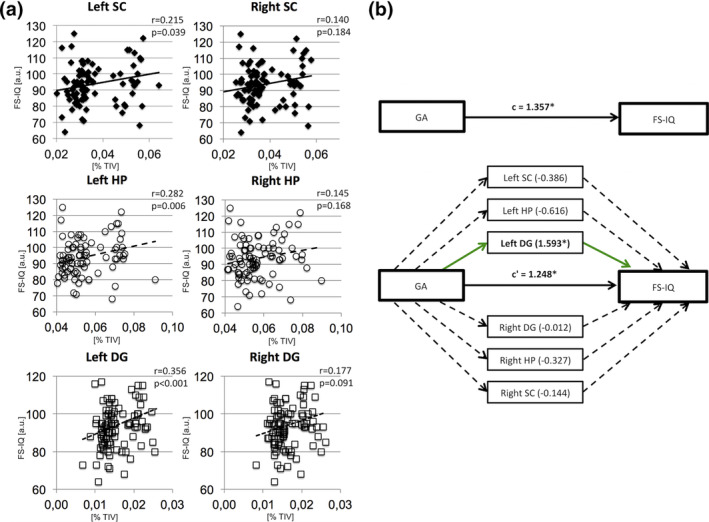
(a) Associations between functional hippocampus unit volumes and adult full‐scale intelligence quotient (FS‐IQ). Scatterplots of associations between left and right SC (upper row), HP (middle row), and DG (lower row) with adult FS‐IQ are shown. Linear regression lines and regression coefficients of partial regression analyses are added. Hippocampus subfield volumes are depicted as percentage of TIV. (b) Left DG volume is a mediator of global cognitive performance. A path diagram is shown in order to illustrate the result of the mediation analyses restricted to the VP/VLBW cohort. Gestational age significantly predicts adult FS‐IQ in the regression model correcting for sex, scanner, and TIV. Bilateral functional hippocampus units were introduced as mediators and left DG volume yielded a significant effect (1.593 ± 0.935; p = .044). The effect of GA on adult FS‐IQ remained significant after introduction of mediator variables. All other functional hippocampus units did not show significant mediating effects. The figure includes the following standardized regression coefficients: c, the total effect of GA on FS‐IQ; c′, the direct effect of GA on FS‐IQ when adjusting for the mediating variables. Significant regression coefficients (p < .05) are marked with an asterisk. DG, dentate gyrus; FS‐IQ, full‐scale intelligence quotient; HP, hippocampus proper; SC, subicular complex; TIV, total intracranial volume; VP/VLBW, very preterm and/or very low birth weight
