Figure 1.
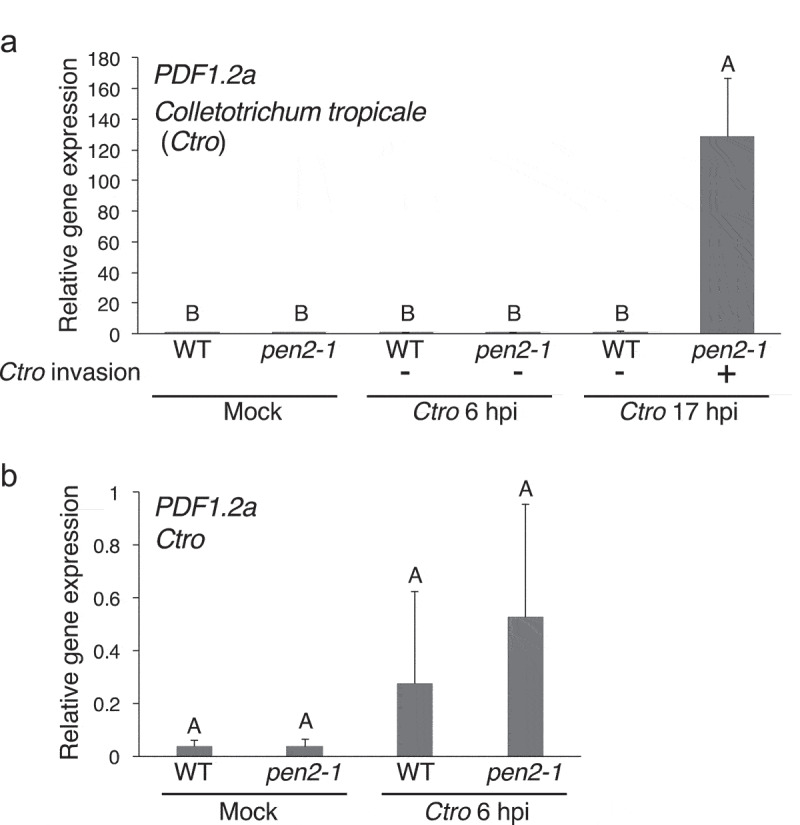
The expression of PDF1.2a was highly induced upon Ctro invasion. a. RT–qPCR analysis of PDF1.2a in Arabidopsis plants inoculated with Ctro. A conidial suspension from Ctro (5 × 105/mL with 0.1% glucose) was spray-inoculated onto 4- to 5-week-old Arabidopsis plants. The leaf samples were collected at 6- and 17-hours post-inoculation (hpi). As a control, 0.1% glucose without Ctro was sprayed onto the plants and the leaf samples were collected at 17 h after this ‘mock’ treatment. Total RNA was extracted using PureLink RNA Mini kits (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and treated with DNase. Takara Prime Script™ RT kits (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) was used for the cDNA synthesis. Takara TB Green™ Premix Ex Taq™ I was used for RT–qPCR with the primers listed in Supplementary Table 1. Arabidopsis UBC21 (At5g25760) was used as an internal control for normalizing the level of cDNA.14 RT–qPCR analysis was performed using a Thermal Cycler Dice Real Time System TP810 (Takara Bio Inc.). Means and standard deviations (SDs) were derived from three independent samples. b. The expression of PDF1.2a was induced at 6 hpi compared with the mock treatment. The RT–qPCR data on mock and Ctro 6 hpi are shown with a different scale on the Y-axis in Figure 1a. The statistical significance of differences in gene expression level was determined by Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test (P < .01). The experiment was repeated twice, with similar results
