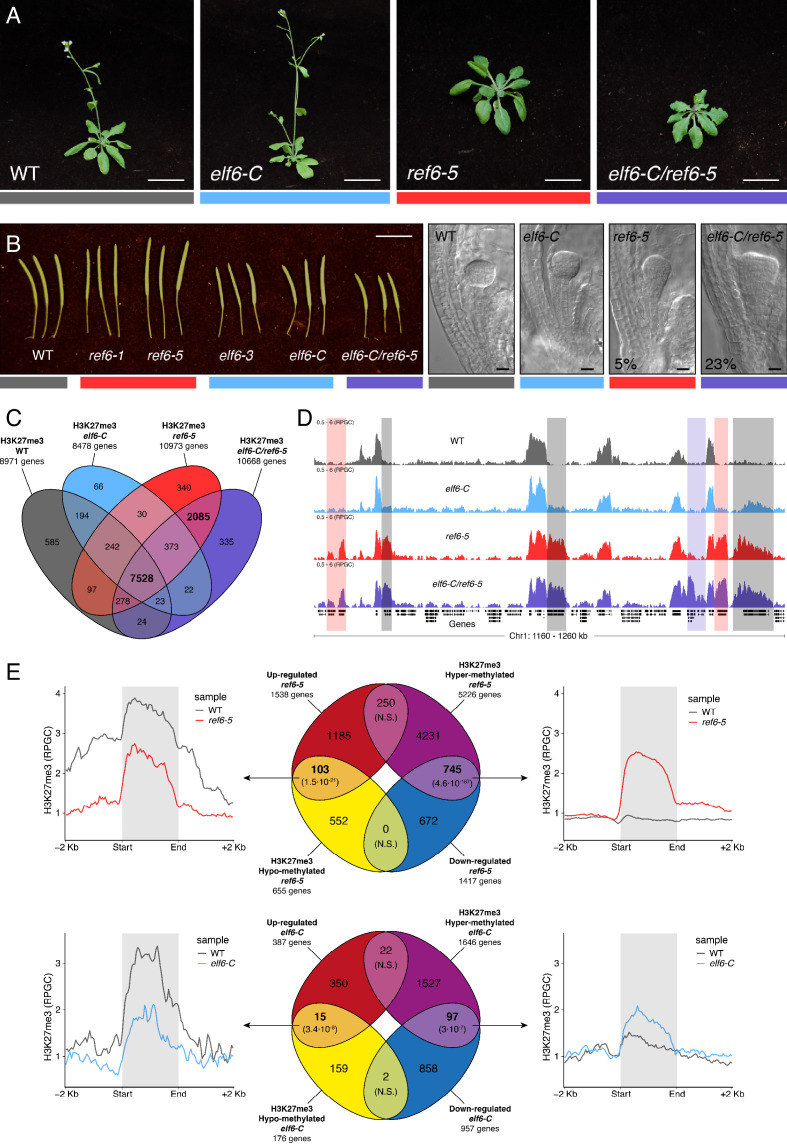
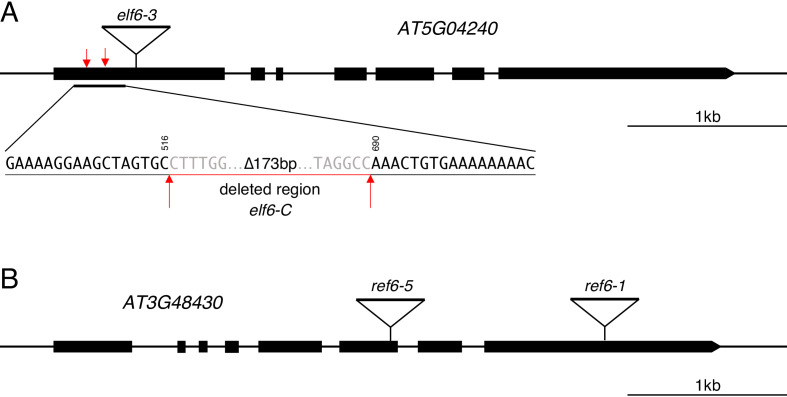
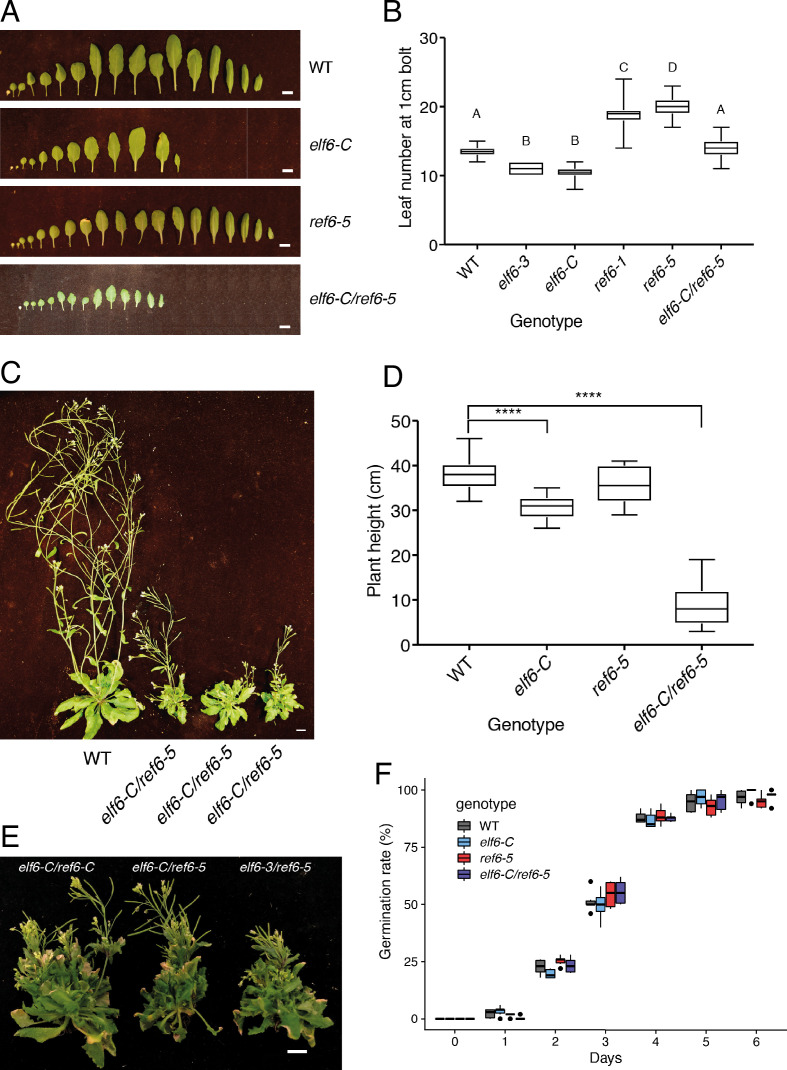
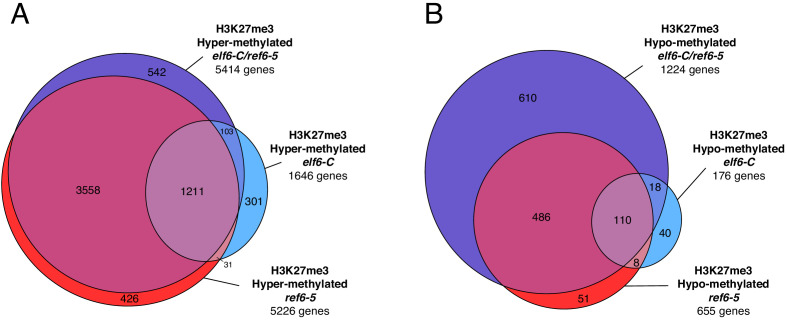
Figure 1. Arabidopsis Histone demethylases ELF6 and REF6 play distinct roles in development and H3K27me3 homeostasis.
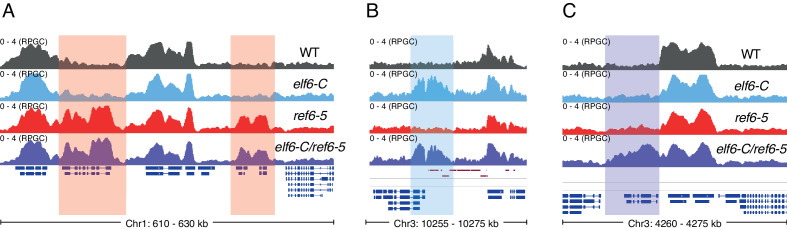
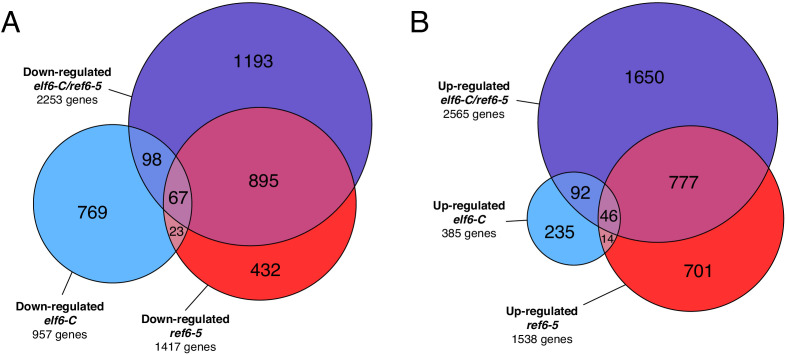
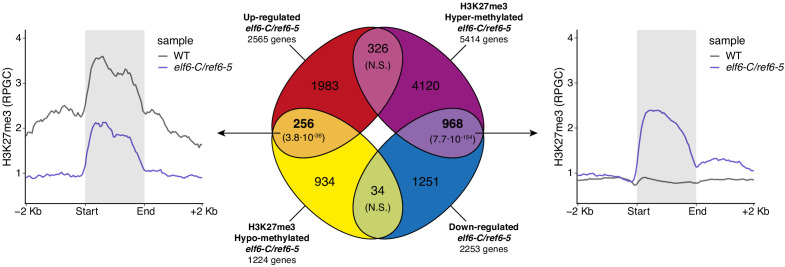
(A) Arabidopsis wild-type (WT) and histone demethylase mutants (elf6-C, ref6-5 and elf6-C/ref6-5). Scale bars, 1 cm. (B) Siliques and embryos from Arabidopsis wild-type (WT) and different mutant alleles of histone demethylase ELF6 and REF6. Numbers show the frequency of the abnormal embryos (n = 250). Scale bars 1 cm and 10 μm, respectively. (C) Venn diagram showing the overlap between genes accumulating H3K27me3 in wild-type (WT) and histone demethylase mutants (elf6-C, ref6-5 and elf6-C/ref6-5). (D) Genome browser views of background subtracted ChIP-seq signals as normalized reads per genomic content (RPGC). Shaded red boxes, genes targeted exclusively by REF6. Shaded grey boxes, genes targeted by REF6 and ELF6. Shaded purple boxes, genes targeted by both REF6 and ELF6, and only hyper-methylated in double mutant elf6-C/ref6-5. (E) Venn diagram showing overlap between differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and H3K27me3 differentially methylated genes in histone demethylase mutants. To the left metaplot for H3K27me3 levels for genes both up-regulated and hypo-methylated and to the right metaplot of H3K27me3 levels in genes both down-regulated and hyper-methylated. Top panel, ref6-5; Bottom panel, elf6-C. p-values for Fisher’s exact test are shown in brackets, N.S. Not Significant.