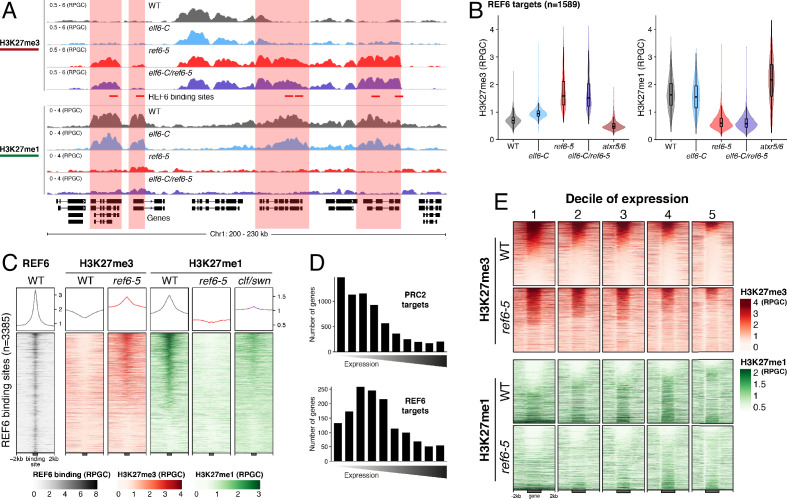
Figure 2. Arabidopsis REF6 plays an essential role in the deposition of H3K27me1 in active chromatin.
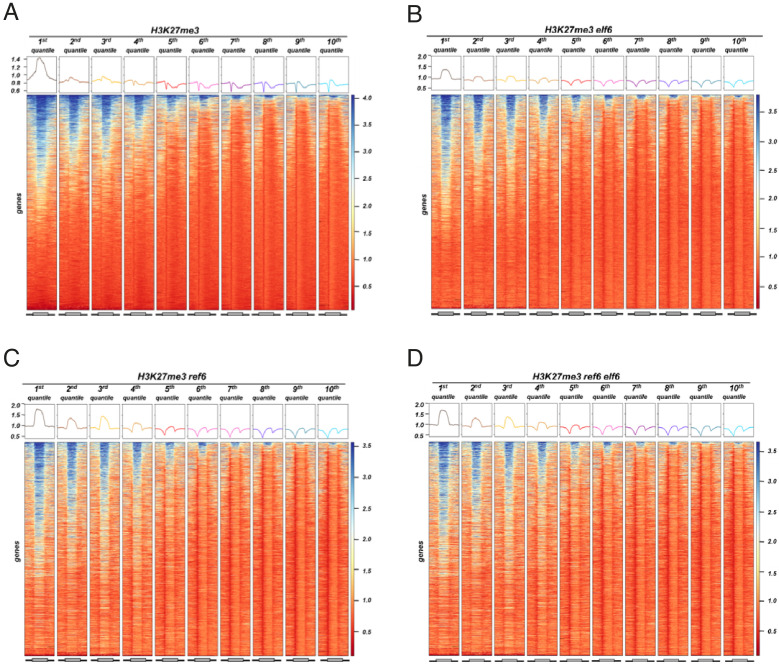
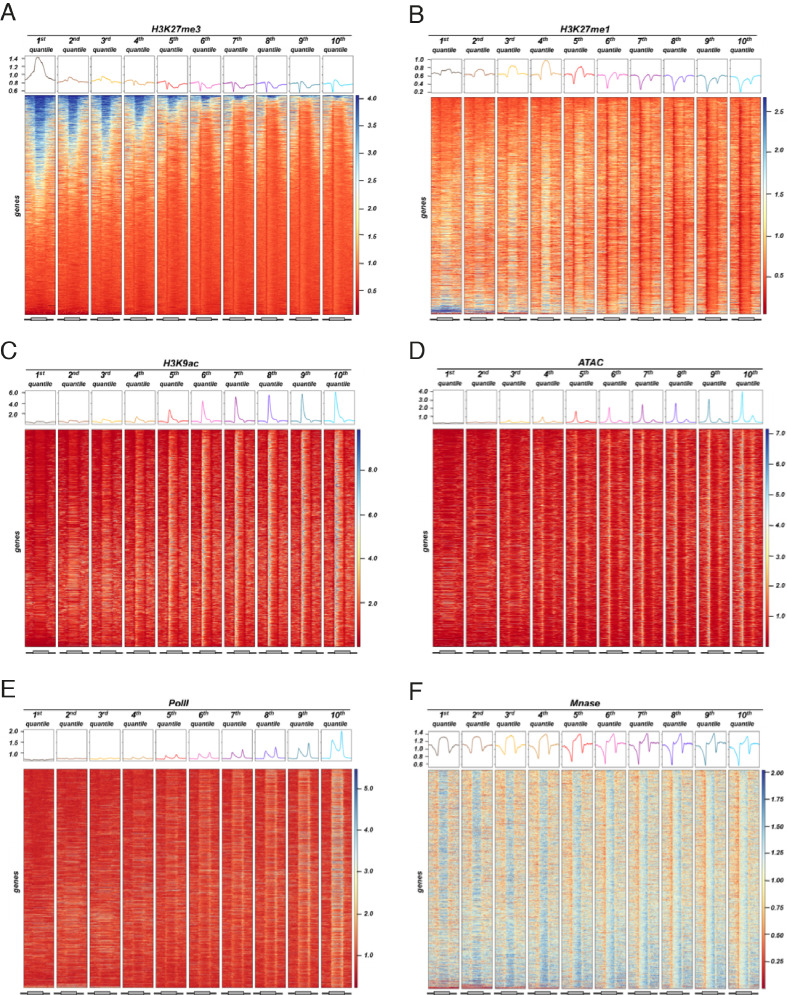
(A) Genome browser views of background subtracted ChIP-seq signals for H3K27me3 and H3K27me1 as normalized reads per genomic content (RPGC) in wild-type (WT) and histone demethylase mutants (elf6-C, ref6-5 and elf6-C/ref6-5). Shaded boxes, genes targeted exclusively by REF6. (B) Violin plots showing the distribution of H3K27me3 and H3K27me1 on genes targeted by REF6. Genes were categorised as targeted if a H3K27me3 peak was annotated on them in ref6-5 and in elf6-C/ref6-5 but not in WT. (C) Heatmap showing the distribution of H3K27me3 and H3K27me1 on genomic sequences targeted by REF6 for wild-type (WT), ref6-5, and clf/swn plants. Sample size n = 3385. (D) Bar charts showing the number of genes for different expression quantiles predicted to be targeted by PRC2 and REF6. (E) Heatmap showing the distribution of H3K27me3 and H3K27me1 present on genes corresponding to low-expression (1-5) quantiles. .
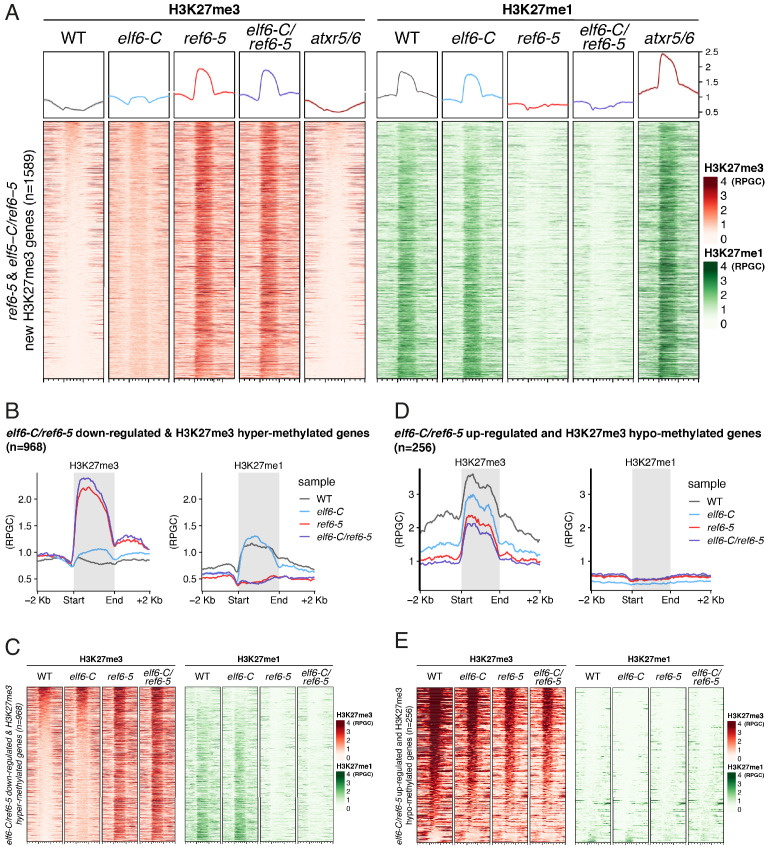
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. REF6 catalyses H3K27me3 to H3K27me1 conversion in genes causing de-repression.
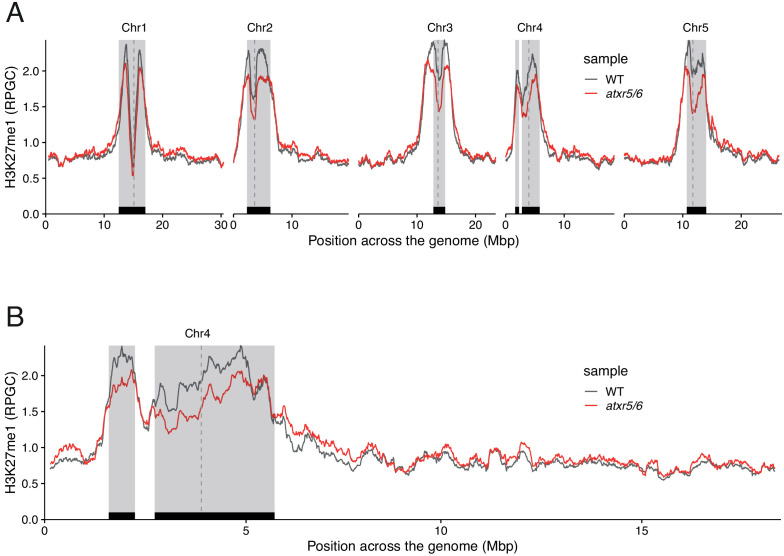
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. ATXR5/6 contributes to the deposition of H3K27me1 in pericentromeric regions.
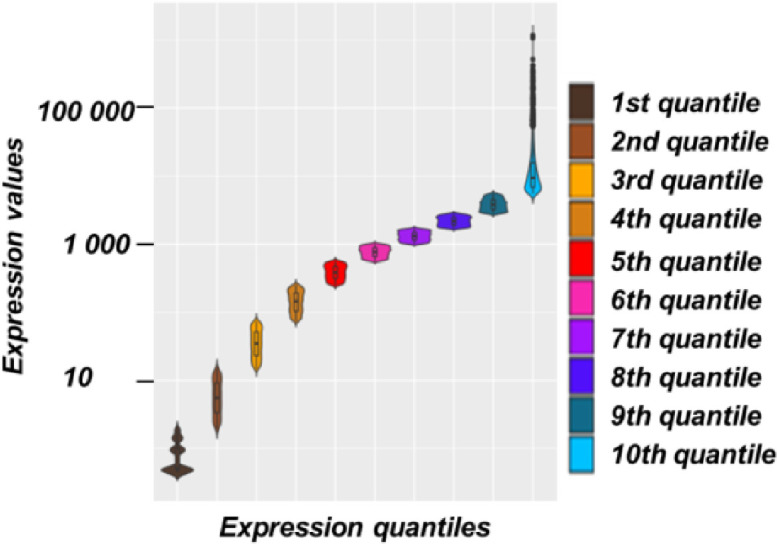
Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Division of Arabidopsis genes according to their levels of expression.