Figure 2. Osteoclasts increase glycolytic flux.
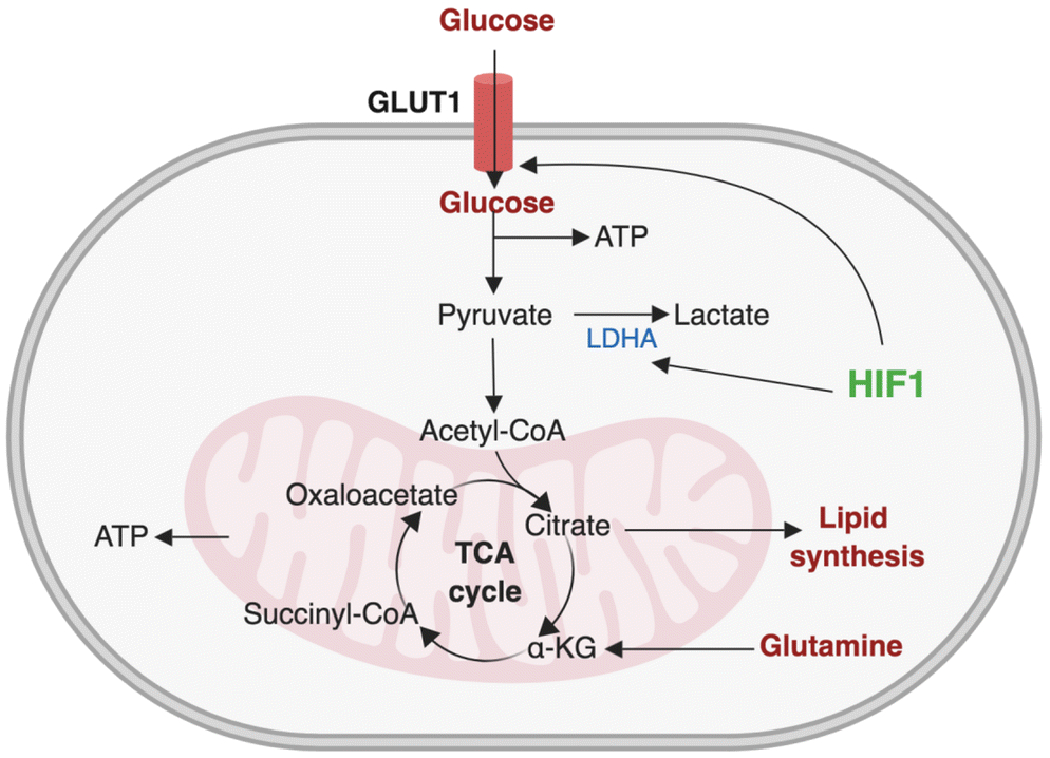
Extracellular glucose crosses plasma membrane via GLUT1. Glycolysis converts glucose to pyruvate, producing two molecules of ATP in the process. Pyruvate then enters mitochondria and the production of most mitochondrial ATP takes place through a series of reactions known as TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle). HIF1 regulates the expression of glycolytic genes including GLUT1 and LDHA. TCA cycle intermediate citrate is used for lipid synthesis and acetyl-CoA is converted into fatty acid by fatty acid synthesis and cholesterol. Glutamine is converted into alpha-ketoglutarate (α-KG).
