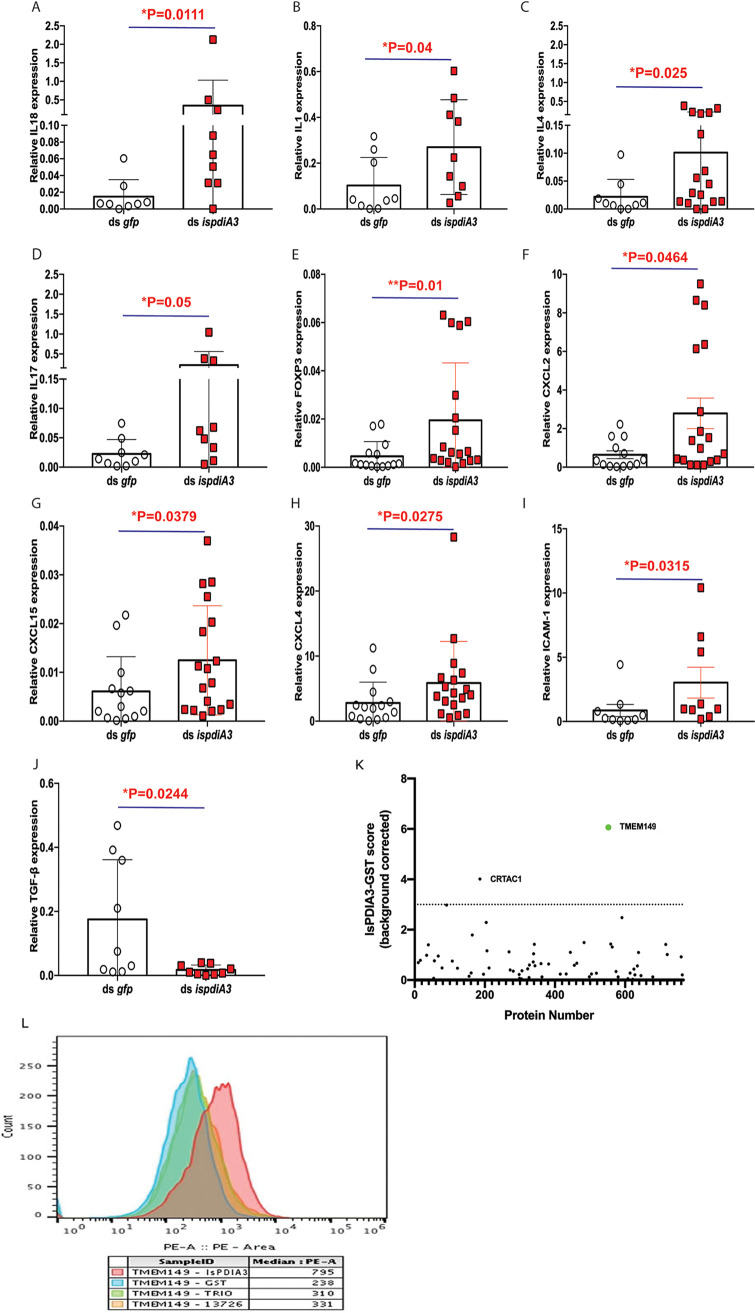
FIG 7.
RNAi-mediated knockdown of IsPDIA3 results in an increased inflammatory response at the tick bite site. Clean nymphs microinjected with ds ispdia3 or ds gfp were fed on clean mice to assess expression profiles of cytokines and chemokines by qRT-PCR at 72 h post tick feeding. Expression profiles of (A) interleukin 18 (IL-18), (B) IL-1β, (C) IL-4, (D) IL-17, (E) FOXP3, (F) CXCL2, (G) CXCL15, (H) CXCL4, (I) ICAM-1, and (J) TGF-β. All of these cytokine and chemokine levels in skin tissues were normalized to mouse β-actin RNA levels according to threshold cycle (2−ΔCT) calculations. Data are averages of 3 biological replicates. Results represent mean ± SD of values. Statistical significance was assessed using a nonparametric Mann-Whitney test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (K) Screening for rIsPDIA3 interactants by yeast display and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) data show 2 proteins. TMEM149 and CRTAC1, that enriched with rIsPDIA3-GST. (L) FACS assessment of TMEM149 binding to rIsPDIA3-GST, rGST, and GST-tagged Anopheles gambiae salivary proteins TRIO (AGAP001374) or 13726 (AGAP013726).