Figure 6.
Endothelin-1 Expression Highly Correlates with Localization of IAHCs
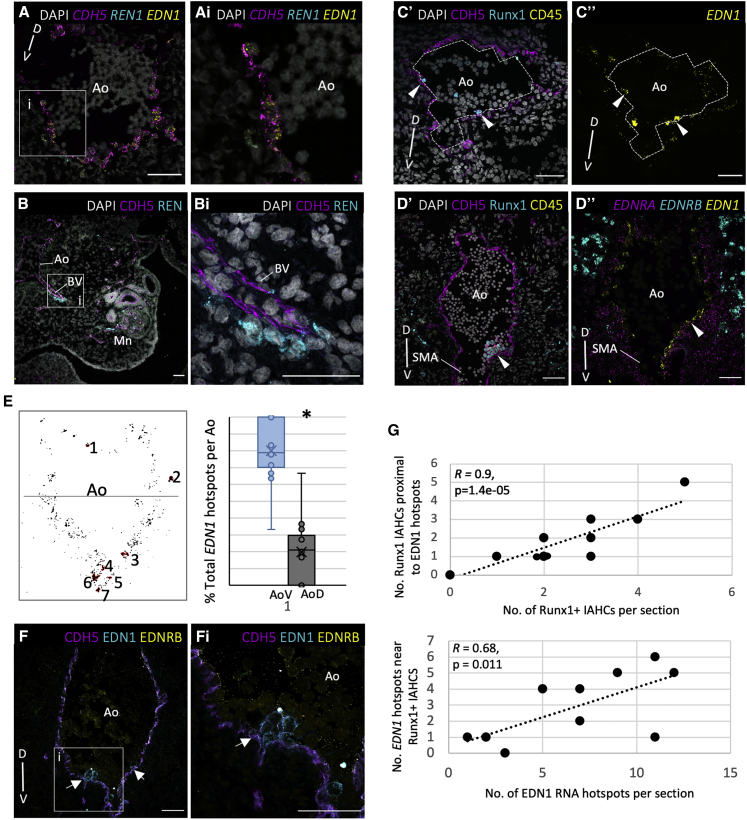
(A) Expression overlap between EDN1, CDH5, and REN1. The arrowhead indicates a REN1+ cell below the CDH5+ endothelium. The images in (Ai) show a magnification of the boxed region in (A).
(B) Expression of REN+ cells enveloping the endothelium of an Ao V branching vessel (BV) directed toward the Mn. The images in (Bi) show a magnification of the boxed region in (B).
(C and D) Immunostaining highlighting V CDH5+Runx1+CD45+ IAHCs (C’ and D’) and, on the sister section, a higher EDN1 signal in a corresponding position (C’’ and D’’). Arrowheads indicate positions of IAHCs.
(E) Representative binary image of EDN1 expression across the Ao with EDN1 hotspots (pixels > 300, 2,048 × 2,048 pixel image) numbered and outlined in red. A line divides the AoD (top) from the AoV (bottom). The box-and-whisker plot shows the percentage of EDN1 hotspots found in the AoV or AoD in each section (n = 14). p < 0.01, t test.
(F) CL of rounded EDN1-expressing cells attached to the CDH5+ endothelial lining (arrows). Images in (Fi) show a magnification of the boxed region in (F).
(G) Correlation between the position of Runx1+ IAHCs in each section with the position of EDN1 hotspots (R, correlation coefficient).
For (A)–(C), (E), and (F), protein or RNA expression is indicated by non-italicized and italicized names, respectively. SMA, superior mesenteric artery. The D-V axis is indicated. Images show transverse sections of CS15–CS16 embryos. Scale bars, 50 μm.