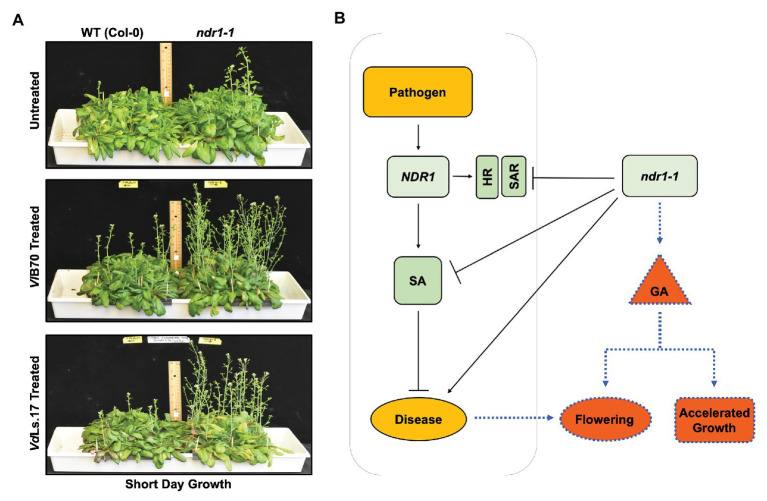
Figure 2.
Verticillium-mediated acceleration in growth and flowering time in Arabidopsis, and the role of NDR1 in mediating hormone cross-talk affecting the growth and defense response. (A) Arabidopsis ndr1-1 mutation causes early flowering in comparison to the wild-type Col-0. ndr1-1 plants grown under short day conditions (10/14 h light/dark cycle) flower early and bolt faster relative to the wild-type Col-0 control plants. A similar phenotype occurs in plants grown under the long day conditions (14/10 h light/dark cycle). Reproduced with permission (Dhar et al., 2019). Arabidopsis ndr1-1 mutants are susceptible to Verticillium longisporum (VlBob70) and flower earlier than the corresponding uninfected plants. Plants of both genotypes were grown under short day conditions and were treated with VlBob70 at a concentration of 5 × 106 conidia/ml applied directly to the soil in the 2nd week of their growth. Picture was taken at 4 weeks post infection. Arabidopsis ndr1-1 mutants are susceptible to Verticillium dahliae (VdLs17) and display flowering earlier than the corresponding uninfected plants. Plants were grown, inoculated, and the picture was taken as described for VlBob70. (B) The ndr1-1 mutant as a tool to dissect hormone cross-talk during pathogen infection. The nonhost specific disease resistance 1 (NDR1) gene is required for defense against biotic and abiotic stresses various plant species. It has also been shown to play an important role in defense and altered growth and development response to infection by pathogenic Verticillium sp. While the Arabidopsis ndr1-1 plants are defective in SA signaling rendering the plant susceptible to pathogenic Verticillium, on the one hand, it leads to early senescence and accelerated growth in a GA-dependent manner, on the other hand (Dhar et al., 2019), thus providing an excellent example of the “growth versus defense” response during pathogen attack. SA, salicylic acid; HR, hypersensitive response; SAR, systemic acquired resistance; GA, gibberellic acid; ndr1-1, nonhost specific disease resistance 1-1 mutant.