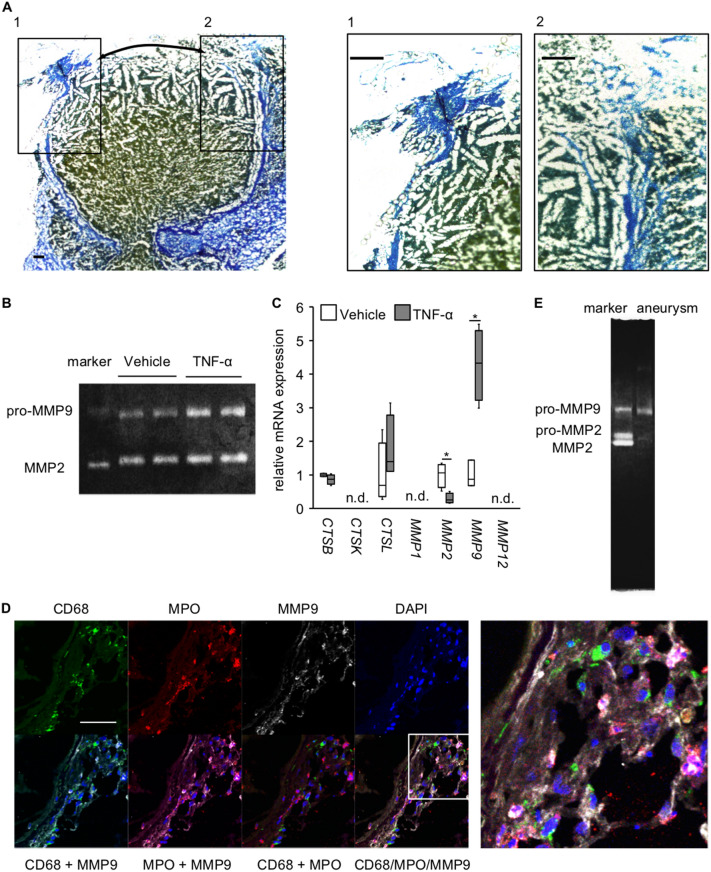
Figure 5.
Production of MMP9 from neutrophils infiltrating in IA lesions. (A) The degenerative changes of collagens around the site of rupture in IA lesions. The representative images of AZAN staining of IA lesions induced in a rat model are shown. Arrows in the left panel indicate the site of rupture. The magnified images corresponding the squares in the left panel are also shown on the right. Bar; 100 μm. (B) Collagenolytic activity of neutrophils. Cultured neutrophils (HL-60 cells) were stimulated with recombinant TNF-α (100 μg/ml, 5 h) and the collagenolytic activity in the supernatant was examined by a gelatin zymography using recombinant pro-MMP9, pro-MMP2 and MMP2 as a reference. The representative image of the gel from a gelatin zymography from 3 independent experiments is shown. The raw image of the gel is shown in Supplementary Figure S3. (C) Induction of MMP9 by TNF-α in neutrophils. Neutrophils were stimulated with recombinant TNF-α (100 ng/ml, 90 min) and the expression of proteinases was examined in RT-PCR analysis (n = 4, except vehicle of MMP9; n = 3). Statistical analysis was done by a Mann–Whitney U test. *; p < 0.05. n.d.; not detectable. (D) Expression of MMP9 in neutrophils infiltrating in lesions. IA lesions were harvested from rats subjected to an IA model and immunostained. The representative images of immunostaining for a macrophage marker, CD68, (green), myeloperoxidase (MPO, red), MMP9 (white), of nuclear staining by DAPI (blue) and merged images are shown. The magnified image corresponding to the square is shown on the right. Bar; 50 μm. (E) Detection of the collagenolytic activity of MMP9 in ruptured IA lesion. Ruptured IA lesions were harvested from rats subjected to an IA model and grinded. Collagenolytic activity was then examined by a gelatin zymography using recombinant pro-MMP9, pro-MMP2 and MMP2 as a reference. The representative image of the gel from a gelatin zymography is shown.