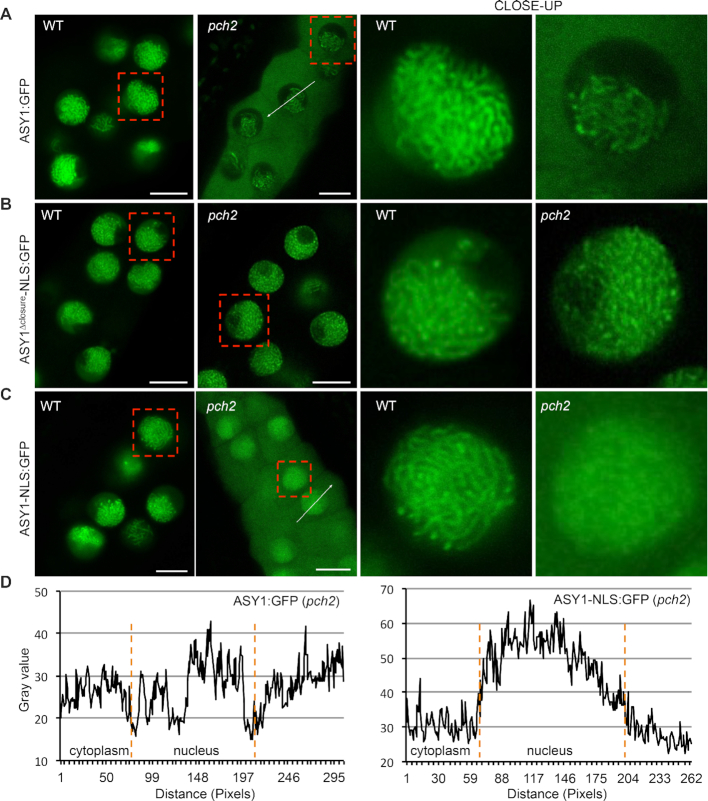
Figure 4.
An interplay between the closure motif and PCH2 controls the nuclear targeting and chromosomal association of ASY1. Localization of ASY1-GFP (A), ASY1Δclosure-NLS:GFP (B), and ASY1-NLS:GFP (C) in male meiocytes of wildtype and pch2 mutants. Bar: 10 μm. Red rectangles highlight the areas of the close-ups. (D) Signal intensity profile of ASY1:GFP and ASY1-NLS:GFP in the cytoplasm and nucleus of pch2 mutants as shown in (A) and (C). The regions used for analysis are highlighted by white arrows in the respective panels. Compared to ASY1:GFP, the greater signal amplitude of ASY1-NLS:GFP in the nucleus than that in the cytoplasm indicates a larger proportion of nucleus-localized ASY1.