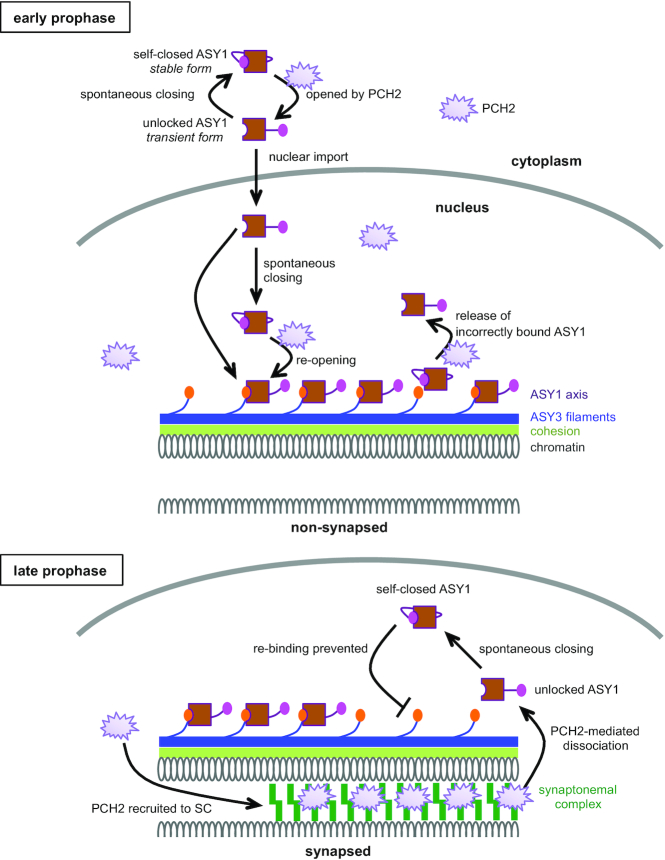
Figure 7.
Model of the PCH2-mediated ASY1 dynamics. At early prophase, PCH2 converts the spontaneously self-closing ASY1 to a transient unlocked form by dissociating the closure motif of ASY1 from its HORMA domain allowing the nuclear import of ASY1. PCH2 is diffusely present in the nucleoplasm ensuring the formation of a pool of unlocked ASY1, which is then loaded onto chromosomes via the binding of the HORMA domain to the closure motif of ASY3 giving rise to closed and stably axis-bound form. In addition, PCH2 appears to play a role in a quality control system by releasing unstably/incorrectly bound ASY1 from the chromosome axis (18). Only one homologous chromosome is shown while the second one is indicated by cut DNA loops. At late prophase when homologous chromosomes synapse, PCH2 is recruited to the synaptonemal complex (SC) from the nucleoplasm. The SC-localized PCH2 removes ASY1 from ASY3 by disrupting the interaction of the closure motif of ASY3 with the HORMA domain of ASY1. The so released transient unlocked ASY1 immediately re-folds into a stable, closed form, thus preventing the re-binding of ASY1 to the chromosome axis.