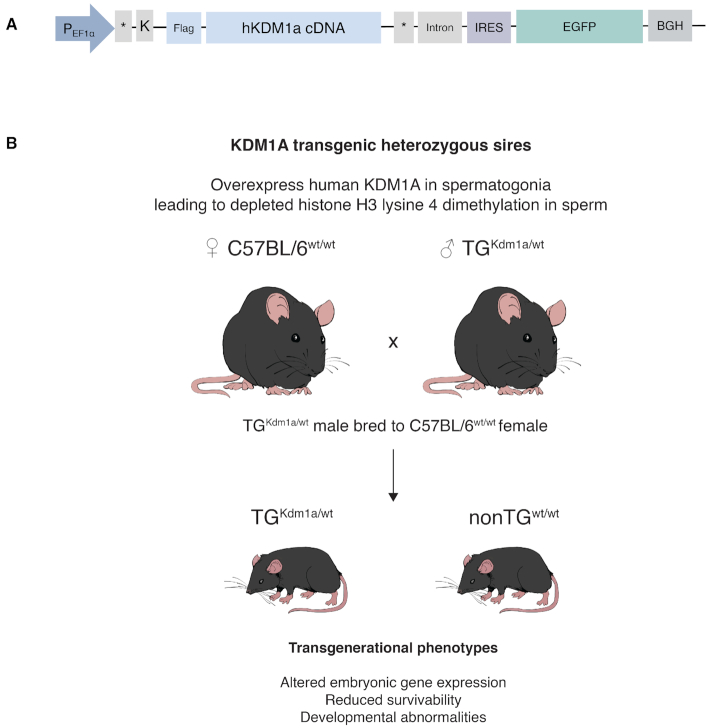
Figure 1.
Transgenic mouse model overexpressing the histone demethylase KDM1A during spermatogenesis is a robust genetic tool to identify the chromatin marks that are associated with transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. (A) Construct used to generate transgenic (TG) male mice on a C57BL6/J background that overexpress human KDM1A during spermatogenesis as described in Siklenka et al. (1). Human KDM1A is expressed under the germ-cell specific truncated human elongation factor 1 alpha promoter (tEF1a). Kozak sequence (K), internal ribosomal entry site (IRES), enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP), and bovine growth hormone (BGH), are found in the polyadenylation signal. (B) Schematic of the transgenic mouse model. Heterozygous TG males have altered histone 3 lysine 4 dimethylation (H3K4me2) at developmental genes in sperm and give rise to transgenic (TG) or wildtype (nonTG) descendants with birth defects. Offspring subsequently sired by TG and nonTG males displayed developmental abnormalities spanning two generations.