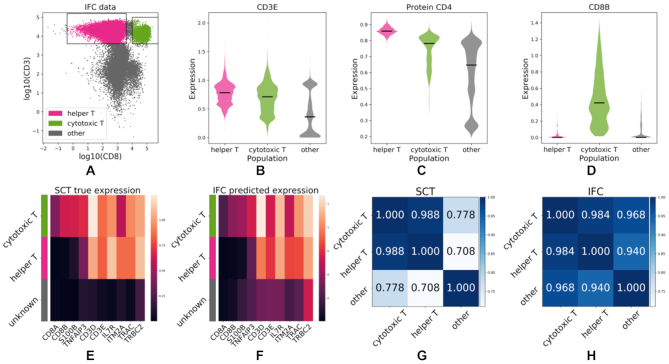
Figure 4.
IFC-seq predicts gene signatures of helper and cytotoxic T-cell subpopulations in human blood mononuclear cells. (A) IFC dataset and corresponding gates for helper and cytotoxic T-cells on the CD3 and CD8 markers. The population of ‘other’ cells corresponds to all unknown cell-types that are not included in the population-specific gates. (B) CD3E, a known T-cell marker is predicted to be highly expressed in both helper and cytotoxic T-cells. (C) Surface CD4, a helper T-cell marker, is predicted to be predominantly expressed in helper T-cells. (D) CD8B, a cytotoxic T-cell marker, is predicted to be almost exclusively expressed on cytotoxic T-cells. (E, F) The expression profiles between marker genes agree across the SCT and IFC experiments. Each row of the heatmap corresponds to a population while each column corresponds to the expression of a gene averaged across all cells in a population. (G, H) The transcriptional similarity of populations is similar across the SCT and IFC modalities. That is, cytotoxic and helper T-cells are more similar to each other than the bulk of other cells.