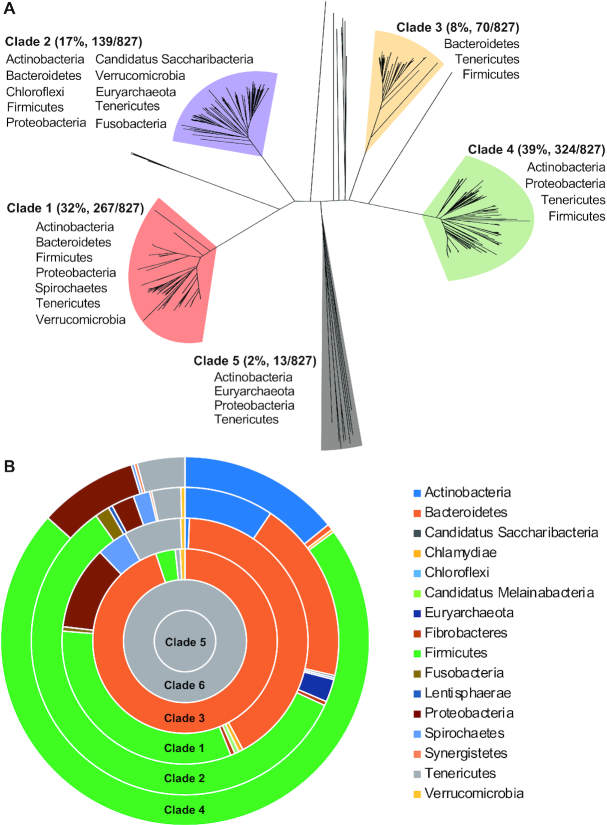
Figure 1.
Sequence diversity and phylogenetic distribution of the inverton-associated invertases. (A) Sequence diversity of the invertase encoded by Type I R-M systems. The invertase homologs encoded by the representative S+ Type I R-M systems initially identified from REBASE (as summarized in Table 1) were used to construct a cladogram by the Neighbor Joining method. The five major clades are colored and labeled with the names of phyla, in which bacteria housing the composite sequences were identified. (B) Phylogenetic distribution of the six invertase clades. The inverton-associated invertase homologs were identified from the NCBI database using the representative proteins of the six invertase clades. Percentage representations of the 16 phyla in the final hits of six clades (as summarized in Table 2) were proportionally presented as colored sections in concentric donuts by Microsoft Excel.