Figure 2.
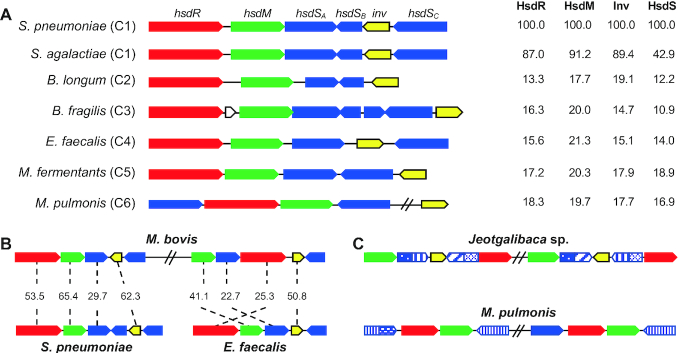
Genetic features of the epigenetic invertons. (A) Schematic illustration of the invertase and R-M genes in seven representative invertase-positive Type I R-M loci from the six invertase clades. The sequences and coding orientations of hsdR (red), hsdM (green), hsdS (blue) and invertase (yellow) genes in each locus are indicated with colored arrows. Percent amino acid sequence homology between each pneumococcal gene and the counterpart of other bacterium is marked on the right side of the gene cluster. (B) Presence of multiple invertons in the same bacteria. Two Type I R-M loci in M. bovis PG45 (accession CP002188) homologous to the invertons from Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus faecalis are schematically displayed as in (A). Percent sequence similarity between the two related sequences (indicated with a dashed line) is provided between each gene pair. (C) Duplication of the invertons. Two Type I R-M loci with identical genetic organization and similar sequences in Jeotgalibaca sp. H21T32 and Mycoplasma pulmonis UAB-CTIP are schematically presented as in (A). The sequences encoding each TRD of the hsdS genes are marked with various patterns of striped rectangles to reflect similarity between the related sequences.