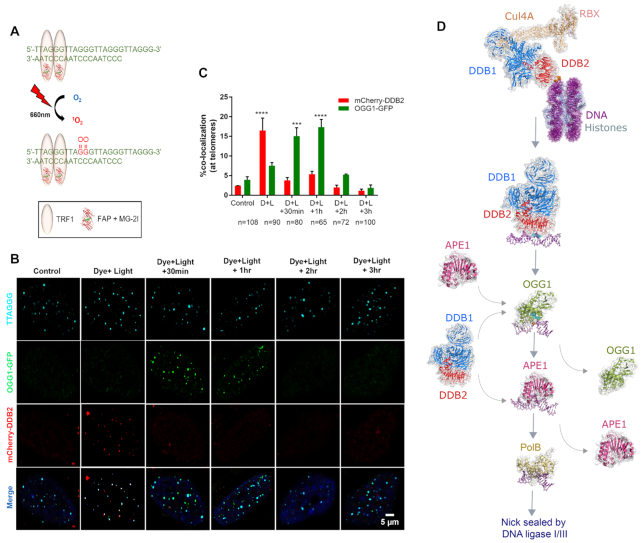
Figure 5.
Role of UV-DDB in 8-oxoguanine (8-oxoG) repair. (A) A chemoptogenetic approach to introduce 8-oxoG at telomeres. Fluorogen-activating peptide (FAP) is fused to a telomere binding protein (TRF1). In the presence of a malachite green dye (MG2I), the FAP-TRF1-MG2I combination is excitable at far red wavelength (660nm) and generates singlet oxygen. Singlet oxygen reacts with telomeric DNA to form 8-oxoG lesions. (B) Immunofluorescence images of mCherry-DDB2 (red) and OGG1-GFP (green) recruitment to and departure from 8-oxoG lesions at telomeres (blue). (C) Quantitative analysis of immunofluorescence images in (B). (D) Working model of the potential role of UV-DDB in BER of 8-oxoG. Figure adapted from Jang et al. (56) with permission. Model of human UV-DDB-CUL4A-RBX bound to a 6–4 photoproduct in the context of a nucleosome, built from PDB codes: 4A0K and 6R8Y (52,123). Human UV-DDB bound to a THF lesion, PDB: 4E54 (124). Human OGG1 bound to 8-oxoG, PDB: 1EBM (125). Human APE1 bound to a 3′ deoxyribose phosphate moiety, PDB: 5DFF (126). DNA polymerase beta bound to gapped and nicked DNA, PDB: 1BPX (127)