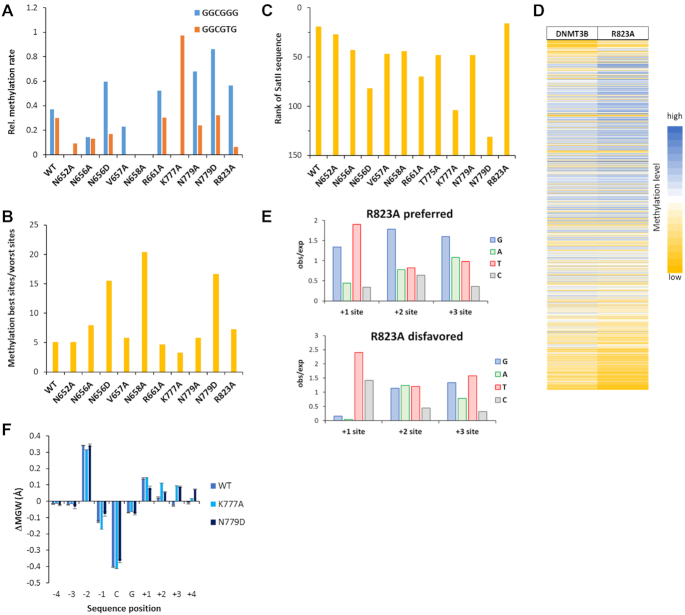
Figure 6.
Effects of amino acid mutations on flanking sequence preferences of DNMT3B. (A) Mutations in DNMT3B increase the flanking sequence sensitivity of CpG methylation leading to a drop in the ability of some DNMT3B mutants to methylate GGCGGG and GGCGTG sequences, here expressed as the ratio of their methylation and the average of all NNCGNN methylation rates. Note that four of the mutations led to a complete loss of GGCGGG and/or GGCGTG methylation (N652A, V657A, N658A and K777A). (B) Ratio of the methylation rates of the 15% best and 15% worst NNCGNN sites. Note, the elevated effects of flanking sequences in N658A, N779D and N656D. (C) Rank of the SatII sequence (TTCGAT) methylation preference by WT and mutant DNMT3B in all 256 NNCGNN flanks. A low rank indicates high methylation activity. (D) Heatmap of the activity of DNMT3B and R823A at the 4096 different NNNCGNNN sequences sorted by the difference in preferences. (E) Occurrence of bases at the +1 to +3 flank sites in the 5% of sequences most preferred and disfavored by R823A. (F) DNA shape effect on the CpG methylation activity of WT DNMT3B and the K777A and N779D mutants. Differences in the minor groove width were determined between the methylated and unmethylated sequences. In both mutants, an increased minor groove width at the +2 to +4 flanks is associated with activity. Data are shown as average of two repeats, error bars indicate the standard deviation.