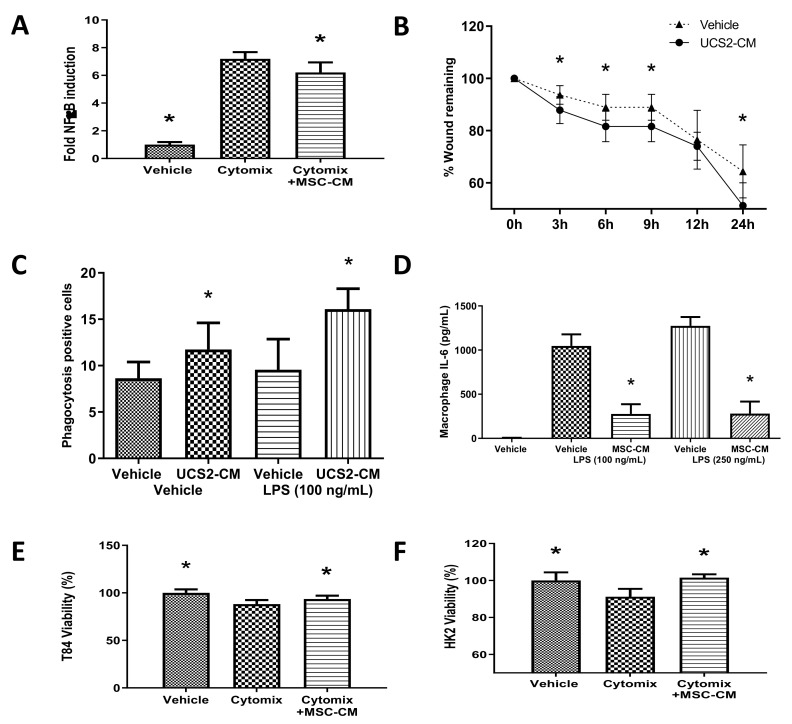
Figure 1.
Anti-inflammatory capacity of CD362+ umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells conditioned medium (UC-MSC-CM) in vitro. CD362+ UC-MSC-CM decreased interleukin 1β (IL-1β)-induced activation of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway (A) and enhanced wound closure (B) in pulmonary epithelial cells. CD362+ UC-MSC-CM increased the rate of phagocytosis in THP-1 macrophages (C) and reduced the production of IL-6 in peritoneal macrophages in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (D). In other sepsis-relevant tissue cells, CD362+ UC-MSC-CM improved viability in kidney-derived HK2 (E) and gut-endothelial-derived T84 cells (F) after cytomix-induced injury. * Statistically significant (p < 0.05) with respect to cytomix group. CD362+ UC-MSCs reduce IL-6 peritoneal macrophage production after LPS stimulation (D). * Statistically significant (p < 0.05) with respect to cytomix (A,E,F), vehicle at (B) or vehicle at same LPS concentration (C,D). Columns represent mean (n = 6), error bars represent SD.