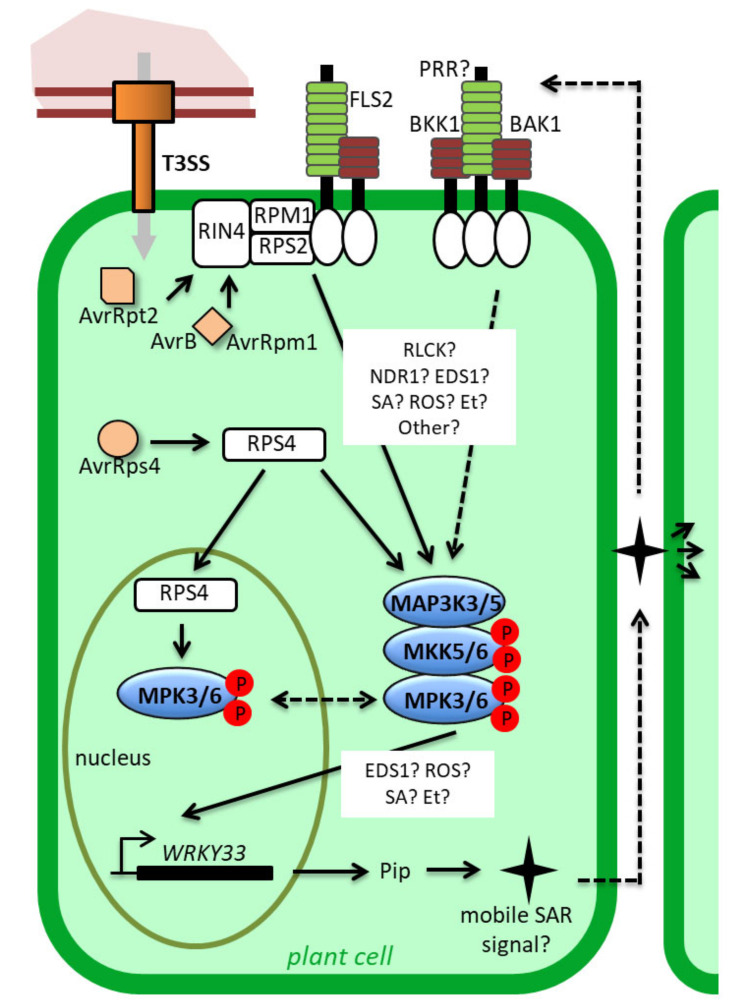
Figure 3.
Representation of the demonstrated and putative mechanisms triggering and regulating sustained MPK3/6 activities in ETI. MPK3/6 are activated upon recognition of the effectors AvrRpt2, AvrB and AvrRpm1 by the CNLs RPS2 and RPM1 in the plasma membrane. The roles of RLCKs, NDR1 and EDS1, as well as SA, ROS and Et signaling, in this process remain to be fully elucidated. MPK3/6 might also be activated upon the recognition of AvrRps4 by the TNL RPS4. This activation might require or lead to the nuclear translocation of MPK3/6. Once activated, MPK3/6 induces the expression of WRKY33 in a manner which may be dependent on EDS1, as well as ROS, SA and Et signaling. At last, WRKY33 expression results in the synthesis of a mobile SAR signaling which is supposed to be recognized by an unknown PRR to trigger a new wave of MPK3/6 activation, thereby consolidating a sustained pattern of activation. For detail, see the main text. Broken arrows and question marks indicate hypothetical actions or components. T3SS: Type 3 Secretory System, PRR: Pattern Recognition Receptor, RLCK: Receptor-Like Cytoplasmic Kinase, Pip: pipecolate.