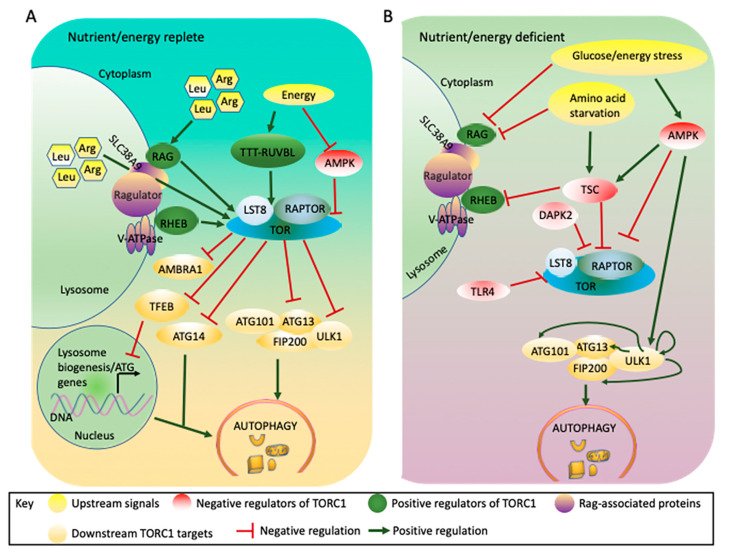
Figure 2.
Mammalian TORC1 integrates signals from nutrients and energy to regulate autophagy. (A). TORC1 is activated by abundant nutrients/energy and phosphorylates components of the autophagy machinery including ULK1, ATG13, ATG14, AMBRA1, and TFEB, blocking autophagy induction. (B). Under nutrient/energy-deficient conditions, TORC1 is inactivated through either TSC or AMPK. Under these conditions, TSC associates with the lysosome and prevents the activation of TORC1 by RHEB, while AMPK phosphorylates RAPTOR and TSC leading to inactivation of TORC1. The loss of TORC1 activity prevents the TORC1-mediated inhibitory phosphorylation of ULK1 and ATG13, while autophosphorylation or AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of ULK1 leads to autophagy induction. Other factors such as DAPK2 phosphorylate RAPTOR under energy stress conditions, leading to autophagy induction, while the TTT-RUVBL complex facilitates TORC1 activation under energy- replete conditions, blocking autophagy induction. AMBRA1: Autophagy/beclin-1 regulator 1; AMPK: adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase; Arg: Arginine; ATG: Autophagy related protein; DAPK2: Death-associated protein kinase 2; FIP200: focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200 kDa; Leu: leucine; LST8: lethal with sec thirteen 8; RAG: Ras-related GTP binding protein; RAPTOR: regulatory associated protein of TOR; RHEB: Ras homolog enriched in brain; SLC38A9: solute carrier family 38; TFEB: transcription factor EB; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; TOR: target of rapamycin; TSC: tuberous sclerosis complex; TTT-RUVBL: Tel2-Tti1-Tti2-RuvB-like AAA ATPase and ATP-dependent DNA helicase complex; ULK1: UNC-51-like kinase 1; V-ATPase: vacuolar-type H+-ATPase.