Figure 1. Endogenous protonmotive force (PMF) regulation.
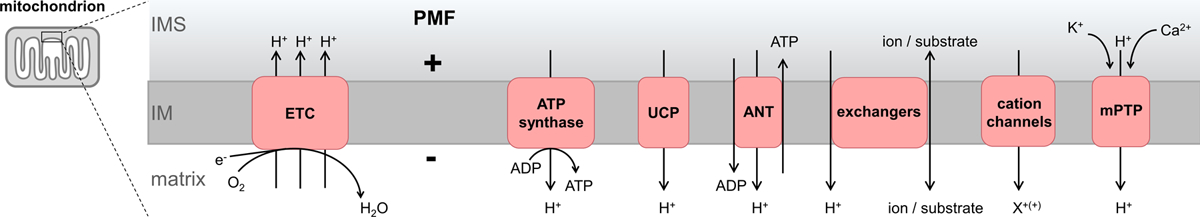
The mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) pumps protons from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space (IMS) to establish the PMF. The PMF drives ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP to ATP. Other proteins in the inner membrane (IM) regulate mitochondrial function through proton transport which affects the PMF. Uncoupling proteins (UCP) are regulated to dissipate the PMF. Similarly, adenine nucleotide transporters (ANT) can also dissipate the PMF in a regulated manner. Several metabolite and ion exchangers also use the PMF to drive their functions. Cation channels in mitochondria can allow cation (X+(+)) accumulation into the matrix. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) is a large conductance channel that can cause total PMF collapse in different physiologic and pathologic conditions.
