Figure 5.
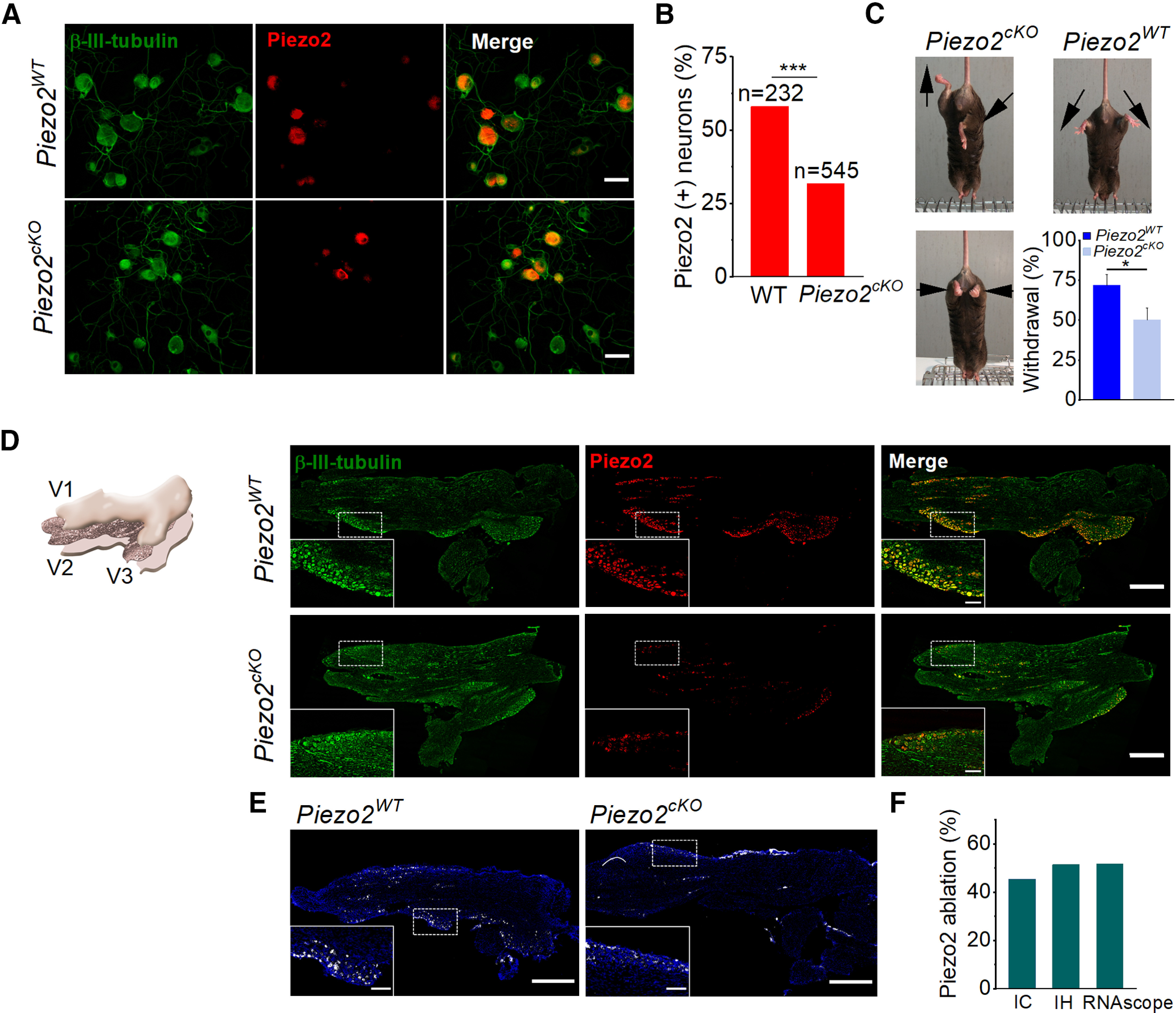
Histologic and functional characterization of Piezo2cKO mice. A, Images of cultured TG neurons immunostained for β-III-tubulin (green) and Piezo2 (red), and merged image from wild-type littermate and Piezo2cKO mice. Scale bars, 50 μm. B, Comparison of the percentage of Piezo2+ neurons in wild-type littermate (n = 2) and Piezo2cKO mice (n = 3; ***p < 0.001; Z-test). Five to seven coverslips were analyzed from each mouse. C, Representative images of leg posture in Piezo2cKO mice (left) when lifted by their tails, showing hindlimb retraction or opposite positioning. None of these postures was observed in their wild-types littermates (right); arrows indicate the orientation of the limbs. The bottom histogram shows the proportion of withdrawal responses to gentle sweep (repeated five times) with a cotton swab over the glabrous surface of the hindpaw in wild-type littermate (n = 9) and Piezo2cKO (n = 9) mice. Error bars represent the SEM. *p = 0.025, Student's t test analysis. D, Schematic representation of the TG, illustrating the plane of section used for immunohistochemistry (left). The three peripheral nerves coming together, V1 (ophthalmic branch), V2 (maxillary branch), and V3 (mandibular branch), are indicated. Representative confocal images of sections of TG immunolabeled for β-III-tubulin (green) and Piezo2 (red), and the merged image in the right panels for wild-type littermates and for Piezo2cKO. Piezo2 neurons only represent a fraction of β-III-tubulin+ TG neurons. Scale bars, 500 µm. Insets show magnified views of the regions marked with the dotted squares. Scale bars, 100 µm. E, Representative confocal images of Piezo2 staining with the RNAscope probe in TG sections from wild-type littermate and Piezo2cKO mice. White, Piezo2 transcripts; blue, DAPI. Scale bar, 500 µm. Insets show magnified views of the regions marked with the dotted squares. Scale bars, 100 µm. F, Histogram shows the percentage of the ablation of Piezo2 in Piezo2cKO mice using immunocytochemistry (IC), immunohistochemistry (IH), and RNAscope in situ hybridization techniques.
