Figure 6.
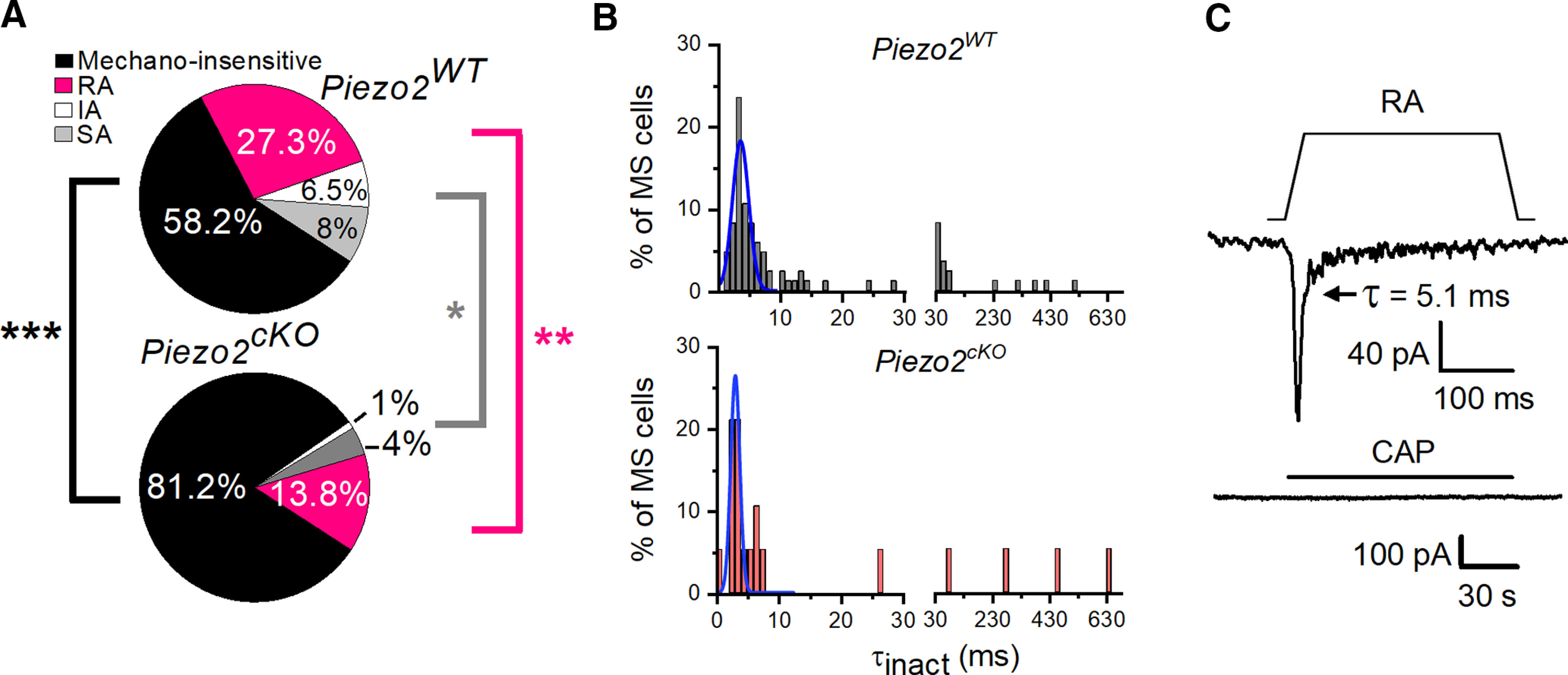
TG corneal mechanosensitive neurons are reduced in Piezo2cKO mice. A, Pie plots show the proportion of mechano-insensitive and mechano-sensitive corneal trigeminal neurons and the distribution of the different types of mechanically activated currents, RA, IA, and SA, in wild-type (top, n = 275) and Piezo2cKO (bottom, n = 101) mice. Black asterisks indicate differences in the proportion of mechano-insensitive neurons. Pink and gray asterisks indicate differences between proportions of RA and IA/SA currents, respectively, for wild-type versus Piezo2cKO mice (***p < 0.001, **p = 0.01, *p = 0.018; Z-test analysis). B, Frequency distribution of inactivation time constants (τinact). Data collected from 85 TG neurons in wild-type and 19 in Piezo2cKO mice, voltage clamped at −60 mV and mechanically activated. Gaussian fits (blue traces) identified only one peak of inactivation time (τ; 3.75 ± 0.26 ms for Piezo2WT mice and 3.05 ± 0.13 ms for Piezo2cKO mice). The bin width was 1 ms up to 30 ms, and 20 ms from 30 ms onward. C, Example of a corneal neuron of Piezo2cKO mice that displayed RA MA currents and did not respond to 100 nm capsaicin (bottom; Vhold = −60 mV). Mechanical stimulus (11 µm) is indicated on top of the recording (top). Time constant of current inactivation is indicated in the panel.
