Figure 8.
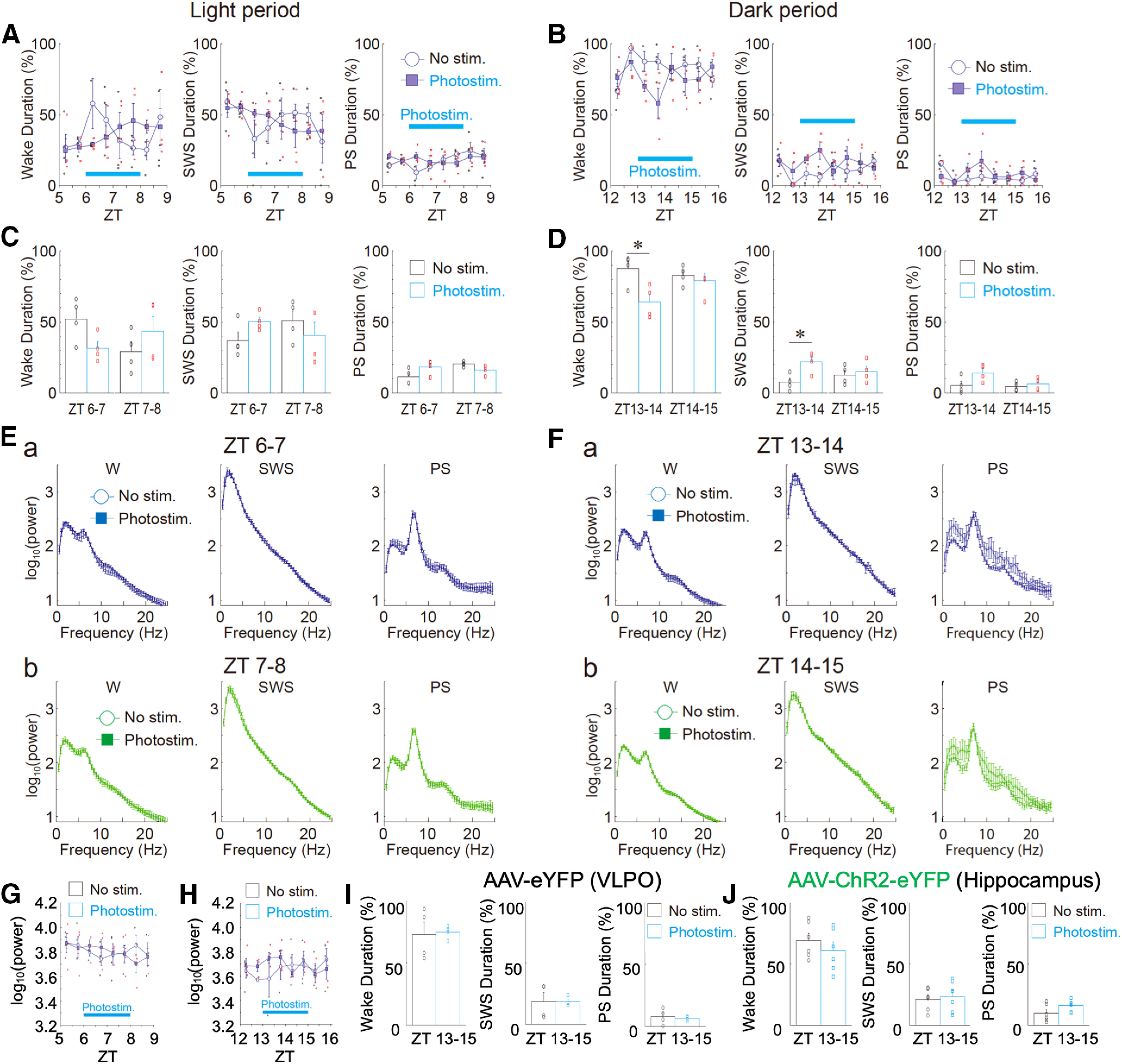
Effects of photostimulation on sleep-wake states and EEG power in light and dark phases. A, B, Changes in the duration of sleep-wake states (wake, SWS, and PS) every 30 min during light [A, zeitgeber time (ZT)5–ZT9] and dark (B, ZT12–ZT16) phases. In these experiments, AAV-ChR2-eYFP was delivered to the VLPO region. Photostimulation was applied to the VLPO region for 120 min (blue bar). Each point and error bar represents the mean and SEM from four experiments. C, D, Photostimulation-induced changes in the duration of sleep-wake states during light (C) and dark (D) phases. Each column and error bar represents the mean and SEM during the first 60 min and the last 60 min of photostimulation. Note that in the first 60 min, but not the last 60 min, photostimulation significantly decreased the wake duration and increased the SWS duration during the dark phase (n = 4, D); *p < 0.05; unpaired t test; wake duration, ZT13–ZT14, t(6) = 3.02, p = 0.0116; SWS duration, ZT13–ZT14, t(6) = 3.18, p = 0.0095. In contrast, sleep-wake states were not significantly affected by photostimulation during the light phase (n = 4, C). E, F, Photostimulation-induced EEG power spectra in sleep-wake states [wake (W), SWS, and PS] during light (E) and dark (F) phases. Note that there was no significant difference in the power spectra between the unstimulated (No Stim) and photostimulated (Photostim) groups. G, H, Changes in δ power in the SWS state every 30 min during light (G) and dark (H) phases. Note that there was no significant difference between the two groups. Each point and error bar represents the mean and SEM from four experiments. I, Effects of photostimulation on the duration of sleep-wake states (wake, SWS, and PS) during the dark phase. The same photostimulation as that shown in B was applied to the VLPO region, but a control virus without ChR2 (AAV-eYFP) was delivered to the VLPO. Each column and error bar represents the mean and SEM from four experiments. J, Effects of photostimulation on the duration of sleep-wake states (wake, SWS, and PS) during the dark phase. The same 120-min photostimulation period shown in B was applied to the hippocampal region, but AAV-ChR2-eYFP was delivered to the hippocampal CA1 region. Each column and error bar represents the mean and SEM from six experiments. Note that photostimulation of ChR2-expressing astrocytes within the hippocampal region had no influence on sleep-wake states.
