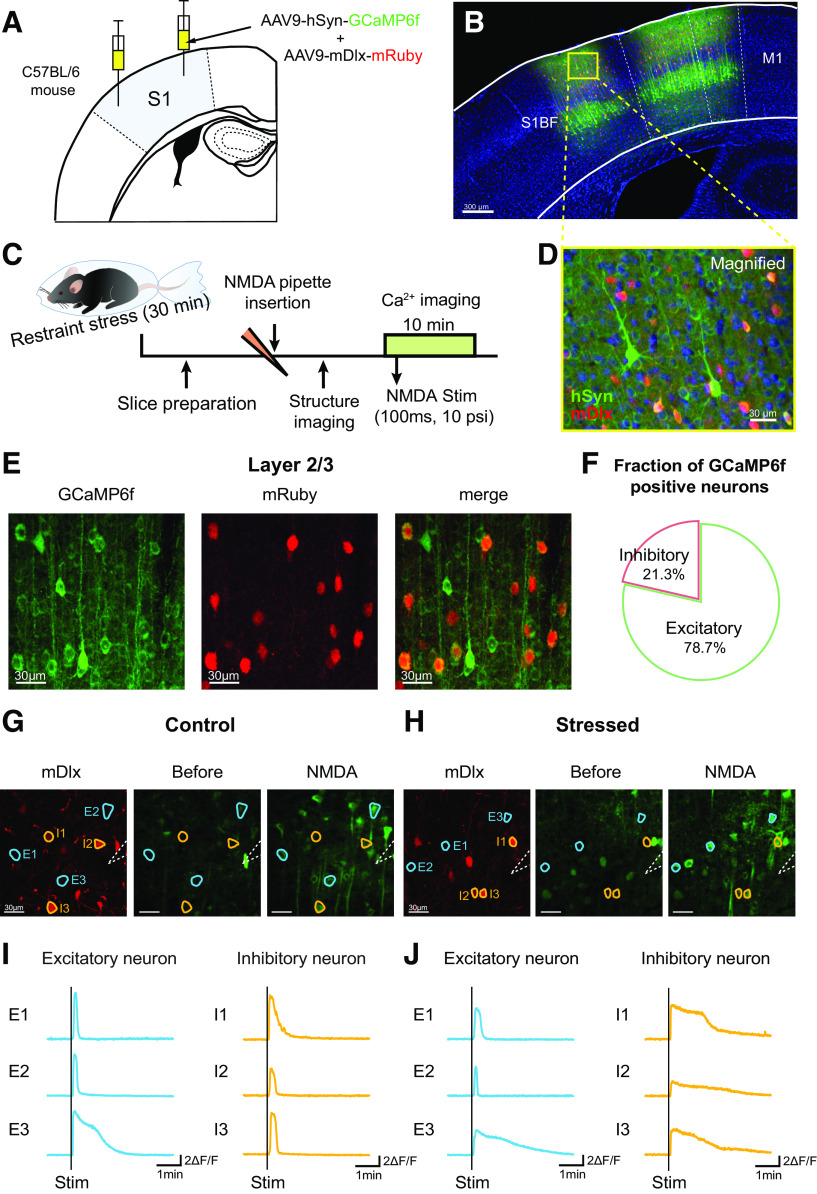
Figure 3.
Ex vivo two-photon calcium imaging of the concurrent calcium transients of excitatory and inhibitory neurons elicited by NMDA stimulation. A, Schematic image showing the protocol for virus injection. A mixture of AAV9-hSyn-GCaMP6f and AAV9-mDlx-mRuby was injected into the primary somatosensory cortex. B, D, Confocal images represent the expression of the injected viral constructs (green represents GCaMP6f; red represents mRuby; blue represents DAPI) in the primary somatosensory cortex. C, Experimental scheme for ex vivo calcium imaging. Two to 3 weeks after virus injection, the mice were immobilized with plastic bags for 30 min, and then ex vivo calcium imaging was conducted. E, Representative images showing all neurons (labeled with GCaMP6f; left) and inhibitory neurons (labeled with mRuby; middle) in layer 2/3 of the somatosensory cortex and a merged image (right). In the merged image, the yellow cells are inhibitory neurons expressing GCaMP6f. F, Fraction of GCaMP6f-positive neurons that were positive or negative for the mDlx enhancer, a marker of inhibitory neurons, in layer 2/3 of the somatosensory cortex; ∼21.27 ± 2.20% of GCaMP6f-positive neurons were inhibitory neurons (in a total of 25 sections from 7 mice). G, H, Example fluorescence image of mRuby-positive inhibitory neurons imaged at 1040 nm (left). Representative calcium images showing the SD of neural activity (GCaMP6f) before (middle) and after (right) NMDA stimulation in control and stressed mice. White dashed lines indicate the glass pipette filled with 1 mm NMDA solution. Blue-masked cells are representative excitatory cells activated by NMDA. Yellow-masked cells are representative inhibitory cells activated by NMDA. Scale bar, 30 μm. I, J, Example raw calcium transients of blue-masked excitatory (blue) and yellow-masked inhibitory cells (yellow) before and after NMDA stimulation. Black vertical lines indicate the points at which the stimuli were applied. Calibration: vertical, 2 ΔF/F; horizontal, 1 min.